Evaluation indicator system for green mining development based on PSR model
abstract
Building a scientific and reasonable green mining evaluation system is an effective way to promote the development of green mining. On the basis of clarifying the connotation of green mining, and in accordance with the "pressure-state-response" analysis framework, 26 are selected from six aspects: resource constraints, environmental constraints, social development concepts, economic output, social output, technical support and management support. Indicators build an evaluation indicator system for green mining development to guide and promote the development of green mining.

Author and unit
Cui Na, Chen Fang, Qi Jingjing
School of Economics, Central South University of Forestry and Technology
citation styles
:
text
As a basic industry for national economic development, mining plays an irreplaceable role in the modernization process. However, for a long time, the extensive development method of mining has also caused greater damage to the ecological environment. Against the background of ecological civilization construction, China actively promotes the construction of green mines and promotes the green transformation and development of mining industry. Since the Chinese government first proposed "green mining" in 2007, China's green mining has been practiced for more than ten years. It is necessary to build a scientific and reasonable green mining development evaluation index system to guide the development of green mining and facilitate scientific evaluation of China's green mining industry. Evaluation and promote the development of green mining.
With regard to the evaluation index system of green mining, different scholars have carried out research from different perspectives based on different theories and methods. From the perspective of ecological economics and the development of industrial chain, Pan Dongyang puts forward that the economic and environmental effects of related industries upstream and downstream of mineral resources should be considered in the evaluation of green mining industry. Sun Yanhui and others, from the point of view of social recognition of green development, a green mining evaluation index system is constructed, which includes five levels: green mine, green economy, social perception of green mine creation, social cognition of green economy and mining enterprises' attitude towards the establishment of green mine. From the perspective of economy-resources-society-ecology, Huang Jie and others constructed the green development index of mining industry, which includes resource conservation, environment-friendliness, transformation and development, safety and harmony, and determined the index weight by using expert consultation method and analytic hierarchy process. From the perspective of sustainable development, Wuliyasu et al constructed the evaluation index system of green mining industry from five aspects: economic development, resource endowment, environmental protection, social support and technical support. Based on APRP (Action-Pressures-Response- Performance) model, Zhou Ling constructed the green mining evaluation index system from four aspects: financial contribution rate of green mining industry, enterprise transformation ability, development ability of green mining industry and regional environmental capacity. With the construction of green mines in China, more and more scholars have carried out research on the evaluation of green mines. Such as Liu Yiqing and others based on the perspective of high-quality development, Ji Lightning and Chen Wansheng have constructed an evaluation index system for the construction of green mines for coal mines. China's Ministry of Natural Resources also issued the "Green Mine Evaluation Index system" in 2020. Generally speaking, there is not much research on the evaluation index system of green mining. Although the green mine is an important part of the green mining industry, the two can not be equated. Compared with the mature green mine evaluation index system, the green mining evaluation system needs to be further studied. In the existing research, the evaluation system of green mining industry is mostly carried out around the idea of "economy-resources-society-environment", but there is a lack of carding and discussion on the relationship between economy, resources and other subsystems in the process of constructing the index system, which leads to the repetition of indicators. the systematicness, scientificalness and rationality of the index system need to be improved. Based on this, on the basis of clarifying the connotation of green mining, this paper constructs the evaluation index system of green mining according to the analysis framework of "pressure-state-response" (Pressure-State-Response, abbreviated as PSR), clarifies the systematic relationship among economy, resources, society and environment.
1 The concept and connotation of green mining
At the end of 1980s, with the introduction and spread of western environmental theory, the green development of mining industry attracted the attention of domestic scholars. In 2000, Shou Jiahua, former vice minister of the Ministry of Land and Resources, put forward the concept of "green mining" for the first time, that is, under the premise that the disturbance of mine environment is less than the regional environmental capacity, the optimization of mineral resources development and the minimization of eco-environmental impact are realized. On this basis, Qiao Fansheng expanded the concept of green mining from three aspects: industrial links, ways of realization and development goals. he believes that green mining includes not only the development of mineral resources, but also the whole process of mineral survey, mine planning, construction, mineral processing, metallurgy, deep processing, mine closure, reclamation and ecological environment reconstruction. Under the guidance of the scientific concept of development, the green mining industry adopts advanced scientific and technological means, implements strict scientific management, and adopts production modes such as clean production, energy saving and emission reduction, comprehensive utilization of resources, circular economy, etc., to achieve the goals of full and rational utilization of resources, environmental protection, safe production, community harmony and sustainable development of mining economy. Li Guozheng put forward that green mining industry is an organic combination of green concept, green way and green goal. By running the concept of green development through all links of mining industry, the unity of economic, social and ecological benefits of mining development can be achieved. Liu Xiaojuan and others believe that green mining is a development model of mining industry, which gives priority to ecology and realizes the coordinated development of economy, society and ecological environment by adopting resource-saving and environment-friendly technical methods for the development and utilization of mineral resources.
It can be seen that green mining is actually a reflection and transformation of the traditional mining development path, and is essentially a transformation and upgrading of the mining economy. From the perspective of the industrial chain, green mining is not limited to the mining of mineral resources, but also includes the entire mining industry chain such as mineral exploration, development, processing and recycling. Green mining covers a wider range than green mines. Green mining is a "chain" and is the green development of the entire mining industry chain, while green mines are a "point" and only refer to the exploration and development of mineral resources. The two are overall and partial. Relationship; From the perspective of the life cycle of a mine, green mining not only includes mine construction, but also the entire process of mine planning, mine closure, reclamation and ecological reconstruction; From the perspective of realization methods, green mining mainly relies on advanced technical means and strict scientific management to achieve it; from the perspective of the goals pursued, green mining needs to achieve the coordination and unity of resource, environment, social and economic benefits.
2 Construction of green mining development evaluation index system based on PSR model 2.1 PSR model
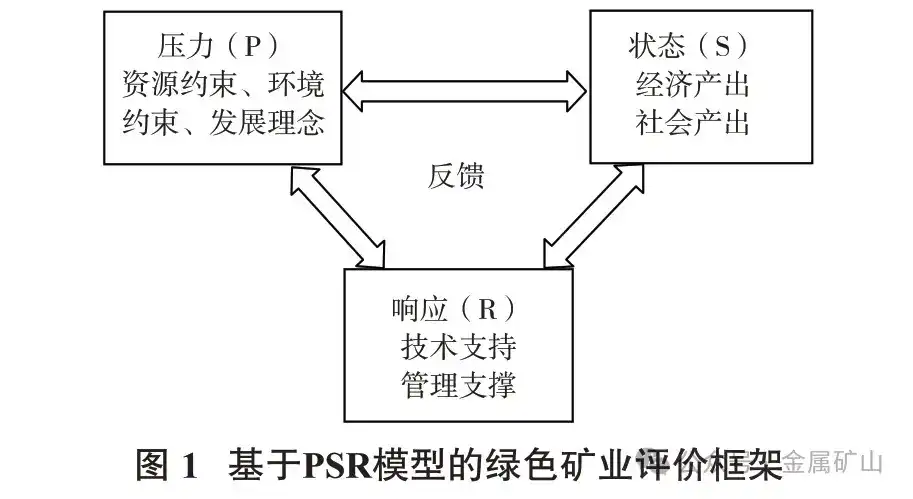
The PSR model is a framework system jointly promoted by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) and the Economic Cooperation and Development Agency (OECD) in the 1980s for studying environmental issues. Among them, P stands for "Pressure", which refers to the loss of resources and environmental pollution caused by human activities;S stands for "State", which refers to the state presented by resource, environment, economic and other systems under specific pressures;R stands for "Response", which refers to the various countermeasures taken by humans to reduce resource consumption and environmental pollution in the face of the aforementioned pressures and conditions.
Pressure-state-response is the relationship of mutual influence and interaction, where P (pressure) is the cause of S (state), S (state) is the result of P (pressure) and the premise and basis of R (response), and R (response) is an improvement made to reduce P (pressure) and improve the current S (state). The PSR model is actually based on a systematic perspective and systematically considers the ecological and environmental pressure, resource and environmental status, and social responses brought by human activities according to causal logic, so as to achieve the coordinated and unified development of social economy and ecological and environmental systems.
2.2 Thoughts on building indicator system
The basic idea of building a green mining evaluation index system is based on the PSR analysis framework, combined with the concept and connotation of green mining, and clarified the pressure, status and response system of developing green mining.
Mining is a basic industry for national economic development. Under the influence of the traditional development concept that puts economic growth first, China's mining industry has always relied on high investment and high consumption of mineral resources to maintain economic growth. This extensive economic growth method not only consumes a large amount of non-renewable mineral resources, but also causes serious environmental pollution. As mankind attaches increasing importance to the ecological environment and population growth, the restrictive effect of resources and environment on economic growth has gradually increased. Green mining has become an inevitable choice for the sustainable development of mining industry. In fact, green mining is a choice made by changes in human development concepts under the constraints of resources and environment. Therefore, the pressure on green mining mainly comes from resource and environmental constraints and changes in social development concepts.
The development state of green mining is the state of mining development under certain resource and environmental constraints, which is reflected in the economic output of mining and the social output brought by mining development.
The response is the response measures taken in response to the development status of the green mining economy under the pressure of resources and environment. The goal pursued by green mining is the coordinated and unified development of ecology, environment, economy and society, and the way to achieve it is to rely on advanced technology and scientific management. Therefore, the response system includes technical support and management support.
Pressure, state, and response systems interact with each other and cause each other, forming an organic feedback loop system that jointly affects the development of green mining, as shown in Figure 1.
 2.3 index system design
2.3 index system design
According to the above-mentioned green mining evaluation framework, in accordance with the principles of systematicness, representativeness, independence, objectivity and comparability, and on the basis of referring to the representative green development evaluation indicator system, select indicators from resources, environment, economy, society, policies, etc., and build a green mining evaluation indicator system. The green mining evaluation indicator system based on the PSR model is divided into four levels: target level, criterion level, element level, and indicator level, as shown in Table 1.
 2.3.1 Pressure system
2.3.1 Pressure system
The three element layers of the pressure system are resource constraints, environmental constraints, and social development concepts.
(1) Resource constraints. Resource constraints mainly refer to the constraints of natural resources on the development of green mining. Natural resources are the material basis and carrier for the development of green mining. From the perspective of natural resources needed for mining development, they mainly include mineral resources, water resources and energy. Therefore, resource constraints mainly include mineral resource constraints, water resource constraints and energy resource constraints, which are measured through mineral resource reserves, water consumption per unit of mining output value, and energy consumption per unit of mining output value respectively. Among them, mineral resource reserves restrict mining development from the quantity of mineral resources; water consumption per unit of mining output value and energy consumption per unit of mining output value measure the level of mining development from the intensity of resource loss, which both represent the resource constraint pressure faced by the development of green mining.
(2) Environmental constraints. Environmental constraints mainly refer to the environmental pollution caused by mining development, which is mainly measured by the emissions of "three wastes" during mining production, including emissions of wastewater, waste gas and solid waste. Based on the principle of comparability, exhaust gas emissions per unit of mining output value, wastewater emissions per unit of mining output value, and solid waste emissions per unit of mining output value are selected as indicators.
(3) Social development concepts. People's recognition of the concept of green development is a huge driving force for promoting the green transformation and development of mining industry, and it is also a social pressure faced by mining development and transformation. As an ideology, the concept of social development is difficult to measure directly, but it is easily influenced by publicity and education. Taking into account the principles of data availability and objectivity, green mining promotion expenses were chosen to reflect the social pressure on developing green mining.
2.3.2 Status system
The two element levels of the state system are economic output and social output.
(1) Economic output. Economic output refers to the development status of green mining and can be measured from three aspects: "quantity","quality" and "efficiency". Among them, the "quantity" of green mining is expressed by the total mining output value; the "quality" is analyzed from the industrial structure, that is, the structural relationship between upstream and downstream mining industries, measured by the ratio of mining output value to the total output value of mining processing industry, reflecting the transformation and upgrading effect of mining industry is a reflection of the "quality" of green mining;"Efficiency" refers to the resource utilization efficiency of green mining development under the constraints of resources and environment. It is usually measured by the "three rate" indicators of mining industry, which are mining recovery rate, mining dilution rate and mineral processing recovery rate.
(2) Social output. Social output mainly refers to the impact of green mining development on society, including three aspects: employment opportunities, income impact and tax effects brought by green mining development. The employment opportunities brought by mining are measured by the number of people employed in the mining industry; the income impact is expressed by the ratio of the average wage of people employed in the mining industry to the average wage of people employed in enterprises above designated size; the tax effect is measured by the ratio of resource tax to tax revenue, which represents the contribution of green mining development to social development.
2.3.3 Response system
The two element layers of the response system are technical support and management support.
(1) Technical support. Technical support refers to the advanced technology adopted in the development process of green mining, which is considered from both aspects of technology input and output. Technology investment mainly refers to scientific research funds and personnel investment, which are expressed in terms of the ratio of mining R&D funds to mining output value and the ratio of mining R&D personnel to mining employment. On the one hand, technological output is reflected in scientific research output, and on the other hand, it is reflected in the utilization level of "three wastes" by green mining and the level of environmental governance. Among them, scientific research output is expressed in terms of the number of mining patent applications, reflecting the scientific and technological innovation capabilities and level of green mining; the utilization level of "three wastes" by green mining is measured by the output value of comprehensive utilization products of "three wastes". The level of environmental governance is measured by the mine environmental restoration and governance rate.
(2) Management support. The development of green mining requires strict scientific management. Scientific management includes not only enterprise management, but also public management. Enterprise management is measured by two indicators: the number of mining production safety accidents and the ratio of mining accident deaths to mining employment. It not only reflects the level of enterprise management, but also reflects the extent to which mining companies fulfill their social responsibilities during the development of green mining. Public management is the government's efforts to promote the development of green mining, including three aspects: capital investment, policy support and public services. Capital investment is expressed as the proportion of mining environmental protection investment in fiscal expenditure; policy support is reflected as the number of green mining policies; public services are expressed as the settlement rate of illegal exploration and mining cases. In addition, green mining is an intensive and efficient development method. The intensive management level of mining industry is measured by the proportion of large and medium-sized mining enterprises, which is also the result of scientific management.
3 Conclusion
(1) Building a scientific and reasonable green mining evaluation system is an effective way to promote the development of green mining. By analyzing the concept and connotation of green mining, based on the PSR analysis framework, the pressure sources, performance states and response measures in the development of green mining are clarified, and then 26 indicators are selected to build an evaluation indicator system for green mining development from six aspects: resource constraints, environmental constraints, social development concepts, economic output, social output, and technology support.
(2) Subsequent research will focus on determining indicator weights and collect data for practical application to further improve the scientificity and rationality of the indicator system.
References (omitted)
Please watch, like, and share the triple combo so that more people can see it!
::