Thin liquid film boiling heat dissipation exceeded 2000W/cm², setting a new world record

During the operation of mobile phones, computers, energy storage batteries and other devices and equipment, heating is inevitable. Achieving more efficient heat dissipation is an urgent problem that needs to be solved in many industries. The scientific research team of North China Electric Power University has successfully achieved an ultra-high heat flow density of more than 2000W/cm² in the research on a new heat dissipation mechanism-thin liquid film boiling, setting a new public record currently known at home and abroad, and is expected to further improve the heat dissipation of device equipment. effect. This result was recently published in the authoritative academic journal "International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer".
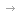
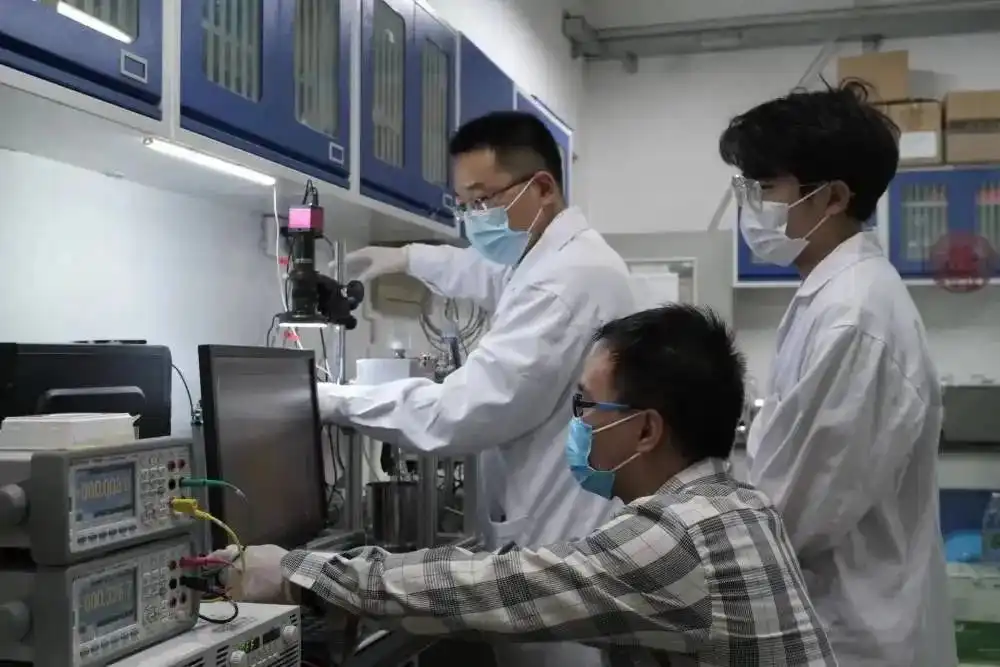 华北电力大学科研团队在调试薄液膜沸腾实验系统。受访者供图
华北电力大学科研团队在调试薄液膜沸腾实验系统。受访者供图
薄液膜沸腾,是目前国际上前沿的可实现超高热流密度散热的方式,即利用冷却液在热源表面形成的超薄液膜持续沸腾,达到高效散热目的。
“一些电子设备运行时,局部发热量可达1000W/cm²以上,显著高于常压下沸水的热流密度,传统的风冷、液冷等方式无法满足散热需求,一定程度上限制了设备性能的提升。”华北电力大学教授、该团队成员冼海珍说,“在实验中实现的2000W/cm²热流密度,相当于在1平方米面积上,1万台功率为2千瓦的电热炉同时发热。”
华北电力大学杜小泽教授、陈林教授是该团队另两名成员。他们介绍,在取得这一实验突破前,国际上已知的薄液膜沸腾研究的热流密度,难以超过1500W/cm²。
团队历经多年研究发现,在恒压供液模式下,用于形成薄液膜的实验样品容易破裂失效,但改为步进增压和连续增压供液后,薄液膜沸腾的临界热流密度最终突破2000W/cm²。由此成功揭示出,优化供液方式,可有效提升薄液膜沸腾的最终性能。该研究成果转化应用后,有望更好保障电子设备、锂电池等的安全性能。
* * *