Defense military R & D pattern and trend under Japan's new security strategy
On December 16, 2022, the Japanese government adopted three revised security policy documents at a cabinet meeting, which involved some guiding contents to improve defense military forces and enhance the military technology foundation. The new security strategy will have a profound impact on Japan's defense military R & D system. This means that Japan will increase its military spending on a large scale and increase its research and development of defense military industries, but this is destined to be a long-term and step-by-step process.
Contents related to defense military research and development in the three security documents
Japan's National Security Strategy is the top-level design of security policies. Among them, the two subsections of "Strengthening the Defense System" and "Strengthening All-round Seamless Protection Measures" in the "Strategic Methods and Main Strategies that Compose the Strategic Method" section both involve the content of Japanese military research and development.
The "Strengthening the Defense System" section mainly includes:Thoroughly strengthen the defense force as the ultimate guarantee for national security; strengthen cooperation in the comprehensive defense system; strengthen the defense production and technical foundation as the defense force itself; and promote the transfer of defense equipment. The "Strengthening all-round seamless protection measures" section mainly includes:Improve response capabilities in the field of cybersecurity; promote maritime security and strengthen maritime security capabilities; strengthen comprehensive aerospace security measures; improve the active use of technology and research and development results in the field of security; strengthen cooperation between the government and the private sector; strengthen Japan's security Information capabilities; strengthen Japan's domestic response capabilities; ensure energy and food and other resources indispensable to Japan's security.
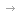
Positioning Japan's National Defense Strategy in the New Strategic System
Japan's "National Defense Strategy" mainly stipulates the following three aspects for Japan's national defense strategic goals:Create a security environment that will never allow the use of force to change the status quo; curb and respond to any attempt to unilaterally change the status quo through force, and clean up the mess as soon as possible; Japan, as the party concerned, must handle, prevent and exclude aggression against Japan. This kind of aggression.
In order to achieve the above goals, the National Defense Strategy believes that Japan's defense capabilities should be strengthened to prevent and eliminate enemy forces 'offensive capabilities from a long distance. When suppression of enemy attacks fails, asymmetric advantages can be gained through cross-regional operations, forcing the other party to abandon its offensive intention. To this end, the following seven capabilities are mainly emphasized:Independent defense capability; integrated air defense missile defense capability; unmanned weapon defense capability; regional joint combat capability; command and control and intelligence capabilities; mobile deployment/national protection capabilities; sustainability/resilience. Among them, the top five capabilities are all related to military R & D and production and military system.

Japan considers using observation activities for security purposes
The National Defense Strategy has more detailed provisions on strengthening Japan's own defense system:Continue to demonstrate the will and ability to restrain opponents from unilaterally changing the status quo; strengthen the response to information warfare including the cognitive field, establish cooperation essentials between the Self-Defense Force, the police, and the Coast Guard, and comprehensively strengthen capabilities in the space, network, and electromagnetic fields; Promote innovation in military high-tech industries and accelerate the application of equipment; based on defense needs, carry out the preparation and strengthening of airports, harbors and other infrastructure to ensure material transportation in sea and airspace; Strengthen cooperation between the Self-Defense Forces and allied countries and partner countries. Although it is also a five-point rule, it is more specific than the previous statement.
According to the new version of the "Defense Capacity Preparation Plan", the Kishida government expects to nearly double defense spending from 1% of GDP to 2% by 2027, totaling 43 trillion yen. Japan's defense spending has also jumped from ranking ninth in the world to third. The core of the new version of the "Defense Force Preparation Plan" is:Strengthen the equipment of the Self-Defense Forces with high-precision and cutting-edge weapons, so that the Self-Defense Forces equipment is at the forefront of the world's major military powers. There is such an expression:"The detection range of foreign radars, the range and performance of various missiles have been significantly improved. By deploying sufficient multi-layered missile defense systems on various locations and platforms, we will improve the ability to suppress armed incursions. When aggression occurs, while ensuring the safety of combatants, the opponent's attack should be stopped as much as possible from outside the threat circle. While improving the manufacturing foundation before 2027, we will promote the rapid application of equipment. Ten years later, while the missile attack range is strengthened, the number of missiles is sufficient."
Trends in Japanese Defense Military Research and Development under the New Security Strategy
Japan's new national security and military defense strategy, represented by Japan's new version of the "National Security Strategy","National Defense Strategy" and "Defense Capacity Preparation Plan", has brought new changes to Japan's security, military and defense policies. It mainly includes the following trends.
Lift restrictions on offensive weapons. 日本新安保和防卫战略解除了二战后对一些进攻性武器的限制,尤其是解除了对远距离攻击导弹的限制。进攻性武器的解禁扩展了日本军工企业的研发项目,更容易获得研发资金,也丰富了日本的军工研发体制自主可控的范围。目前,安保三文件并未对战略轰炸机、大型航空母舰的研发作明确指示,说明日本新在发展进攻性武器方面还有所节制。未来是否会打开“潘多拉魔盒”,有待进一步观察。
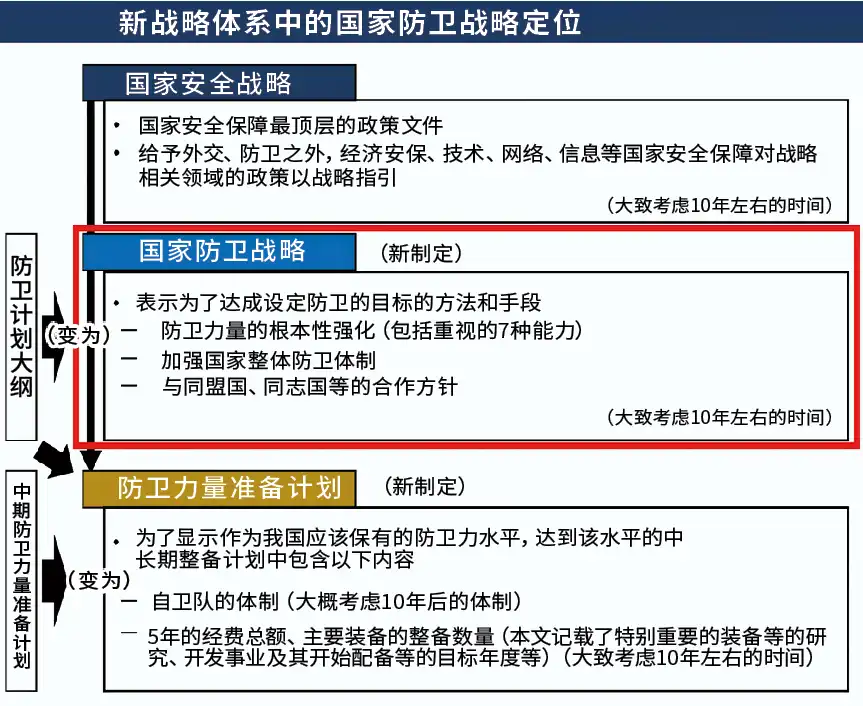
Japan also plans to make efforts in high-tech fields such as unmanned people
Pursuing the development of high-precision and sophisticated technologies and weapons. 日本新安保战略特别强调太空、网络、电磁领域的作战能力,以及无人装备研发。对于日本军工研发体制,尽管他们在这些领域有一定的人才和技术储备,但是要想追上并赶超美国,还需要在人才吸引、人才储备的方面下功夫。在这些领域的研发中,除了要有大量的技术积累还需要投入大量资金,这对于日本国防开支的分配是一种考验。
Further strengthen military cooperation with allies and partner countries. 日本此前与美英法等国家有诸多军工科研合作。要进一步加强与同盟国或者伙伴国家的军工科研合作,需要日本的防卫军工研发体制面向世界,更加开放、灵活。日本现行出口武器的五个种类主要是:救援、运输、警戒、监视和扫雷,暂时还没有出口大型武器。根据《日本经济新闻》报道,日本政府于2023年召开国家安全保障会议,修订“防卫装备转移三原则”的运用指南。这将是自2014年制定“防卫装备转移三原则”以来,日本政府时隔约10年从根本上修改防卫装备出口制度。修改的方向就是可以向海外出售杀伤性武器。这意味着日本对海外武器的出口将可能跃升一个量级,势必推动日本军贸市场需求的扩大以及军工研发体制地位的提升。

Hayabusa 2-Representative of Japan's space capabilities
Ensure Japan's supply of strategic materials and the security of its supply chain. 日本军工科研体制将发挥自身的技术、装备创新优势,研发先进的货轮和货运飞机,以提升节能装备技术水平,增强交通运输能力,助力日本战略物资的供应链安全。
Strengthen cooperation with the military and civilians to jointly ensure national security. 在这个方面,日本防卫省,尤其是防卫装备厅一直在努力。他们通过提供大额资金招聘民间项目,来为日本的军工科技积累长远的人才储备,为军事装备发展指引方向,为掌握前沿科学技术赢得先机,奠定基础。推动军工企业、地方大学和国家公立研究机构开展合作,并不仅仅着眼于眼前获得直接的军工技术和装备,更是瞄准了各领域的科技前沿,长远地培养科技研发的基础,并积累人才。
版权声明:本文刊于2024年 2 期《军事文摘》杂志,作者:周永生、Wang Shan等, If you need to reprint it, please be sure to indicate "Transferred from Military Digest".
attention to our