Wonderful review of the 19th session of "Medicine Precision":Analysis of hot spots in the research and development of tumor ADC drugs, small molecule drugs, and dual antibodies drugs
On March 27, the 19th live broadcast of the innovative drug research and development series video program "Drug Precision" planned and produced by Fanshengzi came to a successful conclusion. This conference invited many experts from innovative pharmaceutical companies, clinical institutions, scientific and technological services, etc. Scholars conducted in-depth exchanges and discussions on hot topics such as the clinical development of tumor ADC drugs, small molecule drugs and dual antibody drugs, as well as the application of concomitant diagnosis in the development of tumor targeted drugs. They shared the latest research results and clinical application experience in their respective fields, attracted hundreds of medical elites to participate, presenting an academic feast for the participants.
Wonderful review of the meeting
Clinical development of HER2 ADC
Wu Zhuli
Senior Vice President of Fosun Pharma's Global R & D Center,
Chief Medical Officer (Oncology), Partner of Fosun Pharma
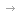
Dr. Wu Zhuli introduced the clinical development of HER2 ADC drugs. In recent years, ADC has become a popular drug in the oncology field and one of the treatment options available after immunotherapy is resistant. It has a very optimistic application prospect in solid tumors. Currently, ADC drugs still focus on HER2 targets. Therefore, when the technology platform is relatively similar, enough differentiation must be made to ensure better safety and efficacy, and a broader range of treatment.
Therefore, for an excellent ADC drug, the first thing to pay attention to is its treatment window. It is affected by many factors such as drug renewal, effects, and linker stability. The narrower the treatment window, the lower the tolerance of the drug may be; Second, attention needs to be paid to its safety management. First, the stability of the linker. Different types of linker have different toxic effects when releasing drugs. Secondly, the carrier of drugs. Different mechanisms of action can lead to different types of toxicities. For example, microtubule inhibitors usually cause blood toxicity and liver toxicity, and the treatment of peripheral nerve toxicity may be more challenging. Third, attention needs to be paid to the recommended dose selection, which determines the balance between the toxicity and efficacy of the drug. If the effect is too strong, it may lead to excessive toxicity, while the effect is too weak, it will affect the efficacy.
Therefore, it is crucial for the drug's payload to have appropriate hydrophobicity to ensure that it can penetrate cells and have a killing effect on nearby tumor cells.
Considerations in clinical design of ADC
Huang Wei
Chief Medical Officer of Shijiazhuang Pharmaceutical Group
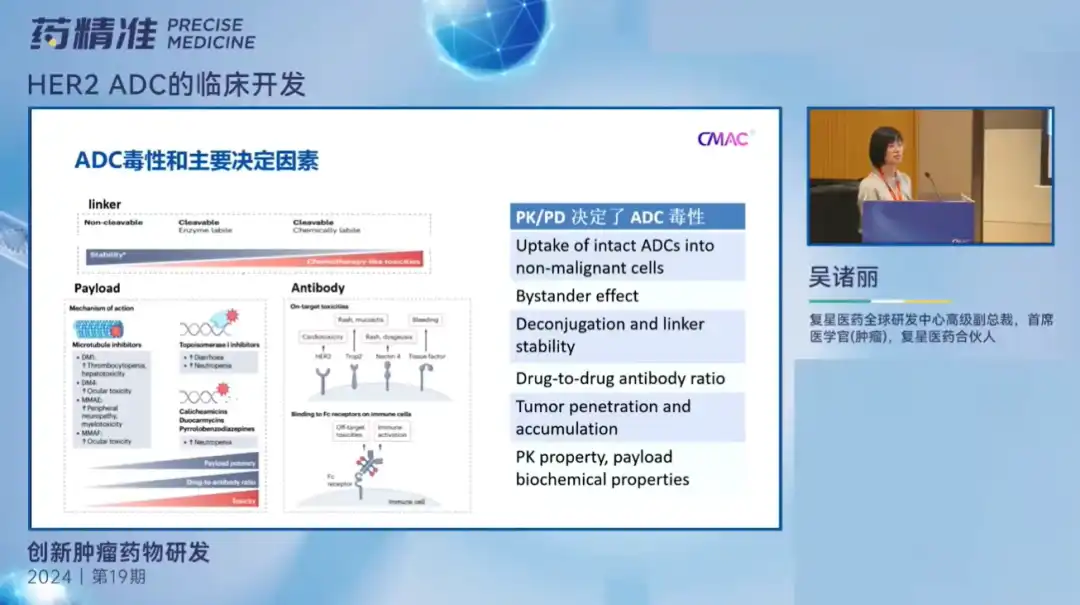
Dr. Huang Wei said that most people in the pharmaceutical industry now pay more attention to product promotion and data, and less attention to the core principles of medical practice. But the strength of the medical team is crucial to the success of the product and the company. Dr. Huang Wei used ADC as an example to explain the considerations in clinical trial design.
Today, the ADC field is growing rapidly, and its targets are extremely important. Based on this current situation, the medical team needs to continuously improve its professional level to cope with industry competition. ADC drugs have evolved from the first generation to the third generation, and medical teams must consider appropriate dose selection, risk sharing issues, clinical needs and treatment mechanisms.
In addition, the selectivity of target antigens, ligand toxicity and optimal dosing regimen are also factors to be considered. Medical teams need to maintain close communication with preclinical teams to ensure preclinical data matches clinical needs. Finally, Dr. Huang Wei pointed out that preclinical data can potentially indicate the effectiveness of drugs in low-or non-expressing populations, so these data need to be carefully analyzed when conducting clinical development.
Progress in clinical research on cancer drugs in China
Wang Shuhang
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Cancer Hospital
Clinical scientist, professor, GCP Center
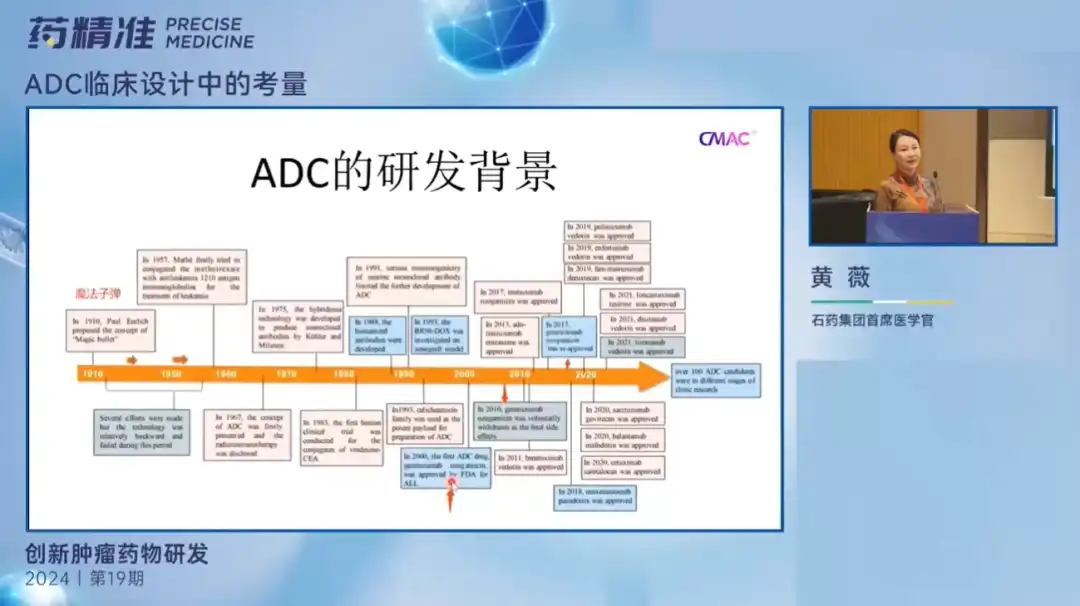
Professor Wang Shuhang shared it online on the forum. She said that China's new oncology drug market is booming, especially in the field of biomedicine. In recent years, increased policy support and corporate investment have promoted the development of the industry, but at the same time, it also needs to deal with the challenge of "involution".
Oncology drugs are still a key area of research and development in China. Most drugs are in the clinical stage, and new targets and combination treatment strategies are receiving attention in cancer treatment. At present, China has performed well in the success rate of new oncology drug research and development, but it still needs to increase the quantity and quality of innovative drug research and development to meet the needs of cancer patients.
In the future, China should cooperate with international medical institutions to conduct global multi-center research, and at the same time learn from foreign experience in review and supervision to improve the quality and efficiency of clinical trials and jointly promote the development of the field of cancer treatment.
Clinical development strategies for tumor-targeted drugs

Zheng Wenjuan
Vice President of Baiji Shenzhou
Head of Solid Tumor Clinical Development in China
Dr. Zheng Wenjuan shared the clinical research strategy of tumor-targeted drugs from three aspects. First, there are two main models of global oncology drug research and development:Joint development and independent development. Joint development usually involves methods such as BD (Business Development) and outsourcing cooperation. This cooperation model can make full use of their respective regional advantages and resource sharing to make clinical research more efficient. On the contrary, independent development requires more conditions, including a professional team of scientists, global clinical development experience, production capabilities and commercial teams. Successful independent R & D needs to be built on the most advanced science-driven innovation pipeline.
In the execution of clinical research, compared with the conventional research path, innovative research design can speed up the research process and speed up the market. This type of model is increasingly used in the oncology field. Second, concomitant diagnostic strategies can accelerate the development of tumor-targeted drugs. Dr. Zheng shared specific cases of osimertinib and pembrolizumab to illustrate how the collection of biomarkers and the development of concomitant diagnoses should be considered in clinical design. Studies have also shown that CDx can more accurately anchor the enrolled population, thereby supporting rapid marketing and effective use of drugs.
In the future, there will be many challenges in the execution of clinical research on tumor-targeted drugs, including patient enrollment, complex research design, and diagnostic techniques. Therefore, the development of clinical oncology drugs needs to make full use of various resources and cooperation opportunities to meet growing challenges, while accelerating the drug development and marketing process.
Biomarkers of dual antibodies in hematological tumors
Li Wenjin
Roche Translational Medicine
Head of Hematology Oncology
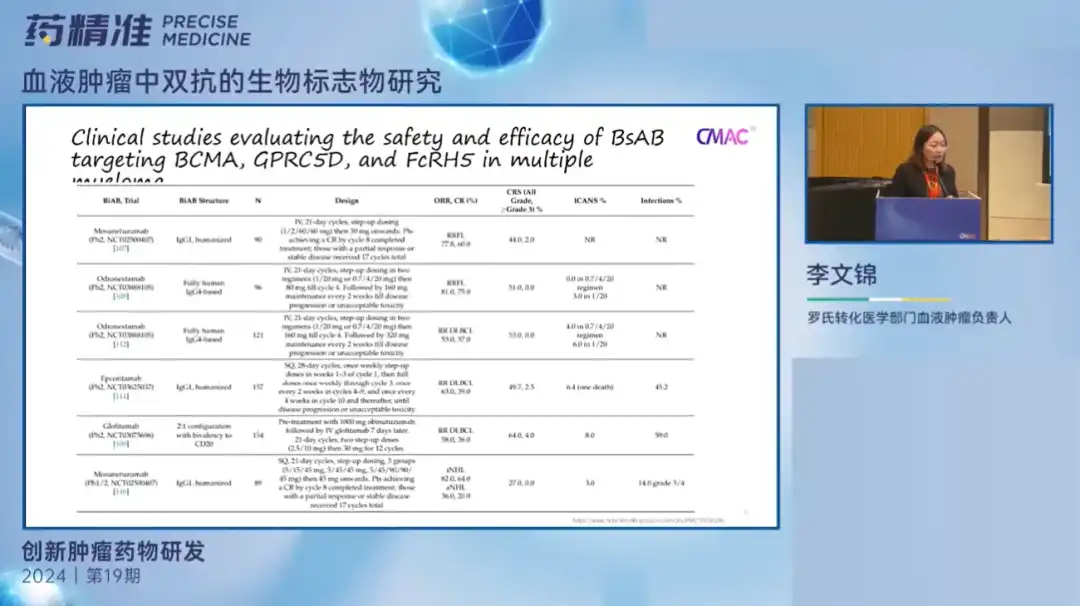
Dr. Li Wenjin introduced the development history of dual antibodies and its importance in the field of drug research and development. In the past few years, new drugs such as bispecific antibodies (BiAbs) and bispecific T-cell binders (BiTEs) have revolutionized the treatment of advanced hematological malignancies.
One of the challenges in the development of BiAbs biomarkers is to evaluate their biological and biochemical effects through target binding and pharmacodynamic (PD) assays to ensure the appropriate dose and dosing regimen are selected. Another important challenge is the loss of target antigens and the promotion of resistance to BiTEs/BiAbs by the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME).
Studies have shown that antigen loss from tumor cells and the presence of an immunosuppressive environment may weaken the efficacy of these drugs, making treatment more complex and difficult. At the same time, using minimal residual lesion (MRD) testing to guide treatment decisions in BiAbs in hematological malignancies can help doctors detect residual cancer cells after treatment early and adjust treatment plans accordingly to improve patient treatment effectiveness and survival rate.
Accompanying diagnosis helps precise drug development
Hu Yunfu
pantheon
Chief Medical Officer
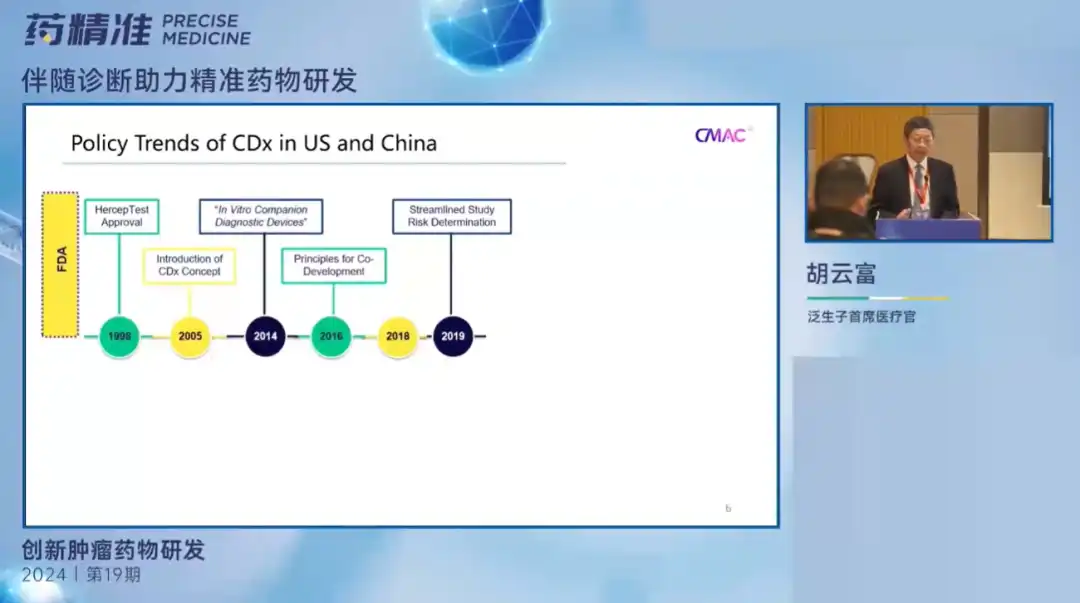
At the meeting, Dr. Hu Yunfu elaborated on the evolution of FDA policies and their impact in the field of diagnostics, and emphasized the importance of diagnostics in drug treatment and the relevant regulations and procedures that need to be followed. Although there are some differences in policies in the field of diagnosis between China and the United States, the requirements for concomitant diagnostic testing standards are very high, and different testing strategies may produce different test results. Taking the development of immunohistochemical kits as an example, when different antibodies are used, different cancer species are detected, different detection instruments and different result interpretation methods are used, the accuracy of the final test results will be affected. Therefore, selecting qualified laboratories and diagnostic methods that can be accurately detected is very important for the development of concomitant diagnosis.
In recent years, proposals for LDT supervision have attracted much attention. In the research on new coronavirus detection reagents, there is evidence that there are differences in test products from different manufacturers. In this case, the supervision of diagnostic testing by regulatory agencies has become more important. Diagnostic reagents with excellent sensitivity and specificity can not only protect the interests of patients, but are also of great significance to drug testing, ensuring accurate test results and accelerating the marketing development of drugs. Now China is also actively responding to the regulatory challenges that accompany the diagnosis, and has successively issued management rules and policies. The "Human PDGFRA Gene D842V Mutation Detection Kit" jointly developed by Pansonzi and Cornerstone Pharmaceutical was approved by the State Food and Drug Administration of China, becoming the first companion diagnostic kit developed using a bridging path.
round-table discussions:Future development trends of small molecule drugs

The roundtable discussion on the future development trends of small molecule drugs was chaired by Dr. Hu Yunfu, and Dr. Zheng Wenjuan, Dr. Li Wenjin, and Dr. Shi Ming, Executive Vice President of Hehuang Pharmaceutical, head of China's R & D and Chief Medical Officer, jointly participated in the discussion. Guests focused on the advantages and market prospects of small molecule drugs, the importance of molecular diagnosis and drug sailing strategies, the development trends and future directions of small molecule drugs in targeted therapy, and the application of molecular diagnosis in the development of hematological tumors and solid tumors drugs were discussed on topics such as application strategies.
Dr. Shi Ming introduced that small molecule drugs currently have certain development experience, and small molecule drugs have relatively complete patent protection policies, which can make strategic arrangements from clinical development to marketing. Dr. Li Wenjin said that due to their unique advantages, small molecule drugs still have broad development space in terms of research and development, production, etc. Dr. Zheng Wenjuan believes that future research focuses will focus on individualized treatment, the application of molecular diagnostic technologies and the exploration of combination treatment strategies. Experts also said that molecular testing plays a key role in all stages of drug research and development, especially in the strategic layout of drugs to sea, and the importance of CDx cannot be ignored.
In recent years, MRD has been an important detection target. It is of great significance in the treatment of both hematological tumors and solid tumors. It can be used to provide treatment guidance, substitute clinical endpoints, etc., and more clinical evidence is needed. At the same time, in the process of small molecule drugs going to sea, the team needs to comprehensively consider the trend of globalization and local regulatory requirements, and select appropriate partners and strategies for layout to achieve global application and commercialization of drugs.
Scan code and enter group communication