2023 Assessment of China's Urban Prosperity and Vitality:In an era of negative growth, urban vitality breaks through
Recently, the China Urban Planning and Design Research Institute released the "2023 China's Urban Prosperity and Vitality Assessment Report."
Cities reflect the trend of China's economy and various changes in the social pattern.
"Asset Insights" here extracts relevant key points of the report for readers 'reference.
————
Negative growth + high liquidity
The core point of the "2023 China's Urban Prosperity and Vitality Assessment Report" of the China Planning Institute lies in "urban prosperity and vitality".
So, how to judge "urban prosperity and vitality"?
The observation point of the Central Planning Institute is:people.
The China Planning Institute believes that a fundamental problem facing the future development of Chinese cities is the population challenge.
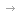
First, China has experienced negative population growth.
At the end of 2022, the country's total population was 1.411 billion, 850,000 less than at the end of 2021, and the natural population growth rate dropped to-0.6 ‰. This is the first time that China has experienced negative population growth since 1961.
Secondly, the scale of population movements is huge.
As China's urbanization process accelerates, population mobility continues to increase. In 2020, the total number of people living in separated households (not living in the place where their registered registration is located) in the country will be close to one-third (376 million, accounting for 27% of the country's total population). The young people aged 20 to 34 are the age group with the highest proportion of household separation. The number of people separated from households is nearly 120 million, and the proportion of household separation is 41%, an increase of 13 percentage points from 2010.
Coupled with the superposition of problems of aging and minority birthrate, today's urban competition for labor has become an important aspect of urban vitality.
Judging from the increase in permanent population, 49 of the 102 large cities across the country will experience negative population growth from 2021 to 2022, and the total population of megacities and Type II large cities will decrease by 0.07% and 0.12% respectively.
Judging from the population growth trend, among the 41 sample cities, only Jinan and Hohhot have seen a slight increase in the average annual increase in permanent population in the past three years in 2022, while the rest have declined to varying degrees. The growth of permanent population in large cities has generally slowed down.
 1962~2022年中国总人口年度变化(万人)(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
1962~2022年中国总人口年度变化(万人)(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
————
36 indicator cities
So, how to observe "urban prosperity and vitality" based on people?
The method of the China Planning Institute is to divide into:Two parts and three indicators.
Two parts--
Resident population and migrant population.
Three indicators--
Reflected in terms of the permanent population, called: Basic vitality of the city;
Reflected by the migrant business population and migrant leisure population, it is called: Functional vitality;
Basic vitality plus functional vitality, called: Comprehensive vitality.
The China Planning Institute selected 36 cities across the country to conduct research.
Including--
10 megacities: Shanghai City, Beijing City, Shenzhen City, Chongqing City, Guangzhou City, Chengdu City, Tianjin City, Hangzhou City, Wuhan City, Dongguan city. 13 megacities: Xi'an City, Nanjing City, Shenyang City, Qingdao City, Changsha City, Jinan City, Zhengzhou City, Kunming City, Harbin City, Dalian City, Hefei City, Foshan City, Suzhou City. 13 Type I cities: NanNing City, Shijiazhuang City, Xiamen City, Taiyuan City, Guiyang City, Urumqi City, Ningbo City, Fuzhou City, Changchun City, Nanchang City, Lanzhou City, Changzhou City, Wuxi City. 4 Type II large cities: Hohhot City, Haikou City, Xining City, Yinchuan. 1 small and medium-sized city: Lhasa City.
————
Comprehensive vitality:Wuhan first
Through research and comparison, the China Planning Institute found that based on the comprehensive vitality of the city, after ranking first in 2022, Wuhan City will rank first again in 2023.
Research shows--
"The comprehensive vitality of cities in East China and Central China has been enhanced as a whole. Except for Nanjing and Nanchang, the comprehensive vitality rankings of 11 cities are flat or higher than last year. Wuhan ranked first, Shanghai and Hangzhou rose to 2nd and 4th, Ningbo rose to 9th, and Changsha, Zhengzhou, Hefei, Qingdao, Jinan, Xiamen and Fuzhou all ranked in the top 20."
"The comprehensive vitality of cities in South China and Southwest China has weakened. The rankings of the three megacities of Chengdu, Guangzhou and Shenzhen fell to 6th, 7th and 10th respectively. Other cities except Chongqing and Haikou also experienced varying degrees of decline."
"The comprehensive vitality of cities in North China, Northeast China, and Northwest China has rebounded. The rankings of Changchun and Shenyang in Northeast China have increased significantly, while the rankings of Beijing, Shijiazhuang and Taiyuan in North China have also increased slightly. The improvement in the vitality rankings of cities in Northwest China has been relatively insignificant."
Top 10 cities in comprehensive vitality1.武汉(华中) 2.上海(华东) 3.北京(华北) 4.杭州(华东) 5.重庆(西南) 6.成都(西南) 7.广州(华南) 8.苏州(华东) 9.宁波(华东) 10.深圳(华南)
Top 10 cities rising in comprehensive vitality ranking重庆(西南)(上升6位) 长春(东北)(上升6位) 福州(华东)(上升5位) 上海(华东)(上升4位) 沈阳(东北)(上升3位) 合肥(华东)(上升2位) 石家庄(华北)(上升2位) 银川(西北)(上升2位) 杭州(华东)(上升1位) 北京(华北)(上升1位)
————
Basic vitality:Wuhan first
The basic vitality is reflected in the permanent population.
Research shows--
"The basic vitality of cities in East China and Southwest China has increased. Among the cities with rapid growth in basic vitality, Hangzhou, Jinan and Fuzhou are all cities in East China, of which Hangzhou is the only megacity with rapid growth in basic vitality. The basic vitality rankings of northern cities including Urumqi, Lanzhou, and Yinchuan have all improved rapidly."
"The basic vitality of cities in South China has declined. Among the cities with rapid decline in basic vitality, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are both cities in South China. Among them, the permanent population of Guangzhou and Shenzhen in 2022 will show negative growth compared with 2021."
The rankings show that the four cities in Beijing, Beijing, Guangzhou and Shenzhen all declined, with Beijing City dropping 9 places, Shanghai City dropping 2 places, Guangzhou City dropping 6 places, and Shenzhen City dropping 5 places. Other cities with large declines include:Nanjing City (down 17 places), Dalian City (down 14 places), Qingdao City (down 8 places), and Xi'an City (down 4 places).
Top 10 cities in basic vitality1.武汉(华中) 2.宁波(华东) 3.厦门(华东) 4.成都(西南) 5.长沙(华中) 6.杭州(华东) 7福州(华东) 8.西安(西北) 9.兰州(西北) 10银川(西北)
Top 10 cities rising in basic vitality ranking济南(华东)(上升8位) 福州(华东)(上升6位) 贵阳(西南)(上升6位) 兰州(西北)(上升6位) 南昌(华东)(上升5位) 乌鲁木齐(西北)(上升4位) 银川(西北)(上升4位) 拉萨(西南)(上升4位) 杭州(华东)(上升3位) 长沙(华中)(上升3位)
————
Functional vitality:Shanghai first
Functional vitality is reflected by the foreign business population and the foreign leisure population.
Research shows--
"The functional vitality of cities in East China and Northeast China has increased. Among the cities with rapid increase in functional vitality, Nanjing, Fuzhou, Xiamen, and Ningbo are all cities in East China, and Harbin, Dalian, and Changchun are all cities in Northeast China.”
"The functional vitality of cities in Southwest and North China has declined."
Cities with rapid decline in functional vitality include Kunming City (down 6 places), Guiyang City (down 5 places), Nanchang City (down 4 places), Zhengzhou City (down 4 places), Chengdu City (down 3 places), Hohhot City (down 3 places), Lan 'Zhou City (down 3 places), etc.
Top 10 cities in functional vitality1.上海(华东) 2.北京(华北) 3.重庆(西南) 4.苏州(华东) 5.广州(华南) 6.杭州(华东) 7.深圳(华南) 8.成都(华南) 9.武汉(华中)、 10天津(华北)
Top 10 cities rising in functional vitality ranking哈尔滨(东北)(上升7位) 长春(东北)(上升4位) 福州(华东)(上升4位) 厦门(华东)(上升4位) 重庆(西南)(上升3位) 天津(华北)(上升3位) 大连(东北)(上升3位) 海口(华南)(上升3位) 南京(华东)(上升2位) 宁波(华东)(上升2位)** **
————
China's four dynamic cities
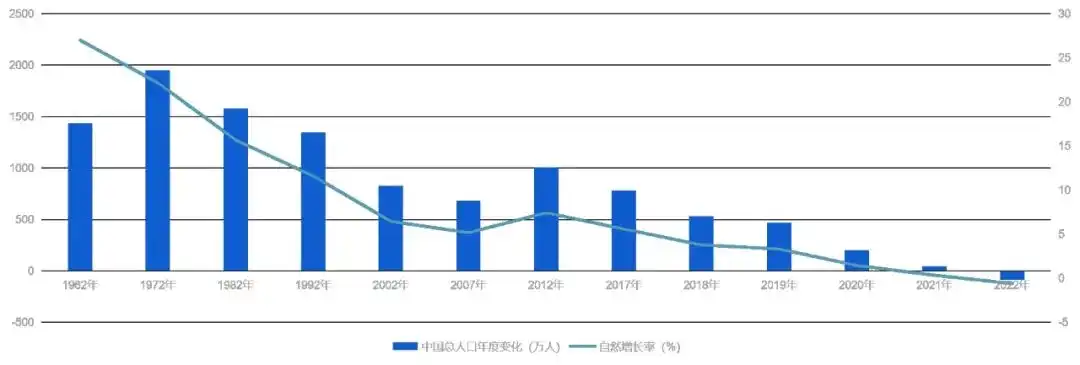
Based on the above research results, the Chinese Academy of Planning has proposed four types of vitality--
1. The stable type (high comprehensive vitality, low basic vitality, and high functional vitality) mainly includes four megacities: Beijing, Shanghai, Chongqing and Guangzhou.
2. Vitality type (high comprehensive vitality, high basic vitality, and high functional vitality) mainly includes Hangzhou, Suzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Wuhan, Chengdu, Changsha, Xi'an, Zhengzhou, Hefei, Fuzhou, Xiamen, Shenzhen, etc.
3. Improved types (medium comprehensive vitality, medium basic vitality, medium functional vitality) mainly include Lanzhou, Yinchuan, Jinan, Changchun, Qingdao, Urumqi, Tianjin, Nanchang, Nanning, Kunming, Haikou, Foshan, Wuxi, Dongguan, etc.
4. Improved type (low comprehensive vitality, low basic vitality, low functional vitality). It mainly includes Taiyuan, Shenyang, Shijiazhuang, Hohhot, Lhasa, Xining, Dalian, Harbin, Guiyang, Changzhou, etc.
 中国城市活力分类(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
中国城市活力分类(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
From 2021 to 2022, some cities have undergone changes in the type of vitality--
1. The average annual increase in the permanent population of Guangzhou (dynamic type → stable type) has slowed down, and the basic vitality of the population has declined. It has shifted from a dynamic type to a stable type similar to Beijing, Shanghai, and Chongqing. 2. The basic vitality and functional vitality of Fuzhou and Xiamen (improved type → dynamic type) have been simultaneously improved, transforming from the original improved type to a dynamic city. 3. Urumqi, Tianjin (upgraded → improved)
Urumqi has been promoted to an improved city due to its improvement in basic vitality; Tianjin has been promoted to an improved city due to its improvement in functional vitality.
————
Urban vitality breaks through
In terms of functional vitality, consumption is an economic projection of urban vitality. Research by the China Planning Institute divides urban merchants into eight categories: natural landscape, cultural landscape, performing arts appreciation, exhibition visits, catering, bars, experience, and leisure, and conducts comparative inspections. Among them, natural landscapes, cultural landscapes, performing arts appreciation, and exhibitions represent the unique vitality of the city. Catering, bars, experience, and leisure represent the city's fireworks. Through further observation, we can see how Chinese cities tap local characteristic resources to lead the restoration of characteristic vitality.
The following are the eight types of commercial cities that have recovered their vitality well and reflected the breakthrough of urban vitality.
Performance appreciation:Shanghai, the "Capital of Performing Arts"
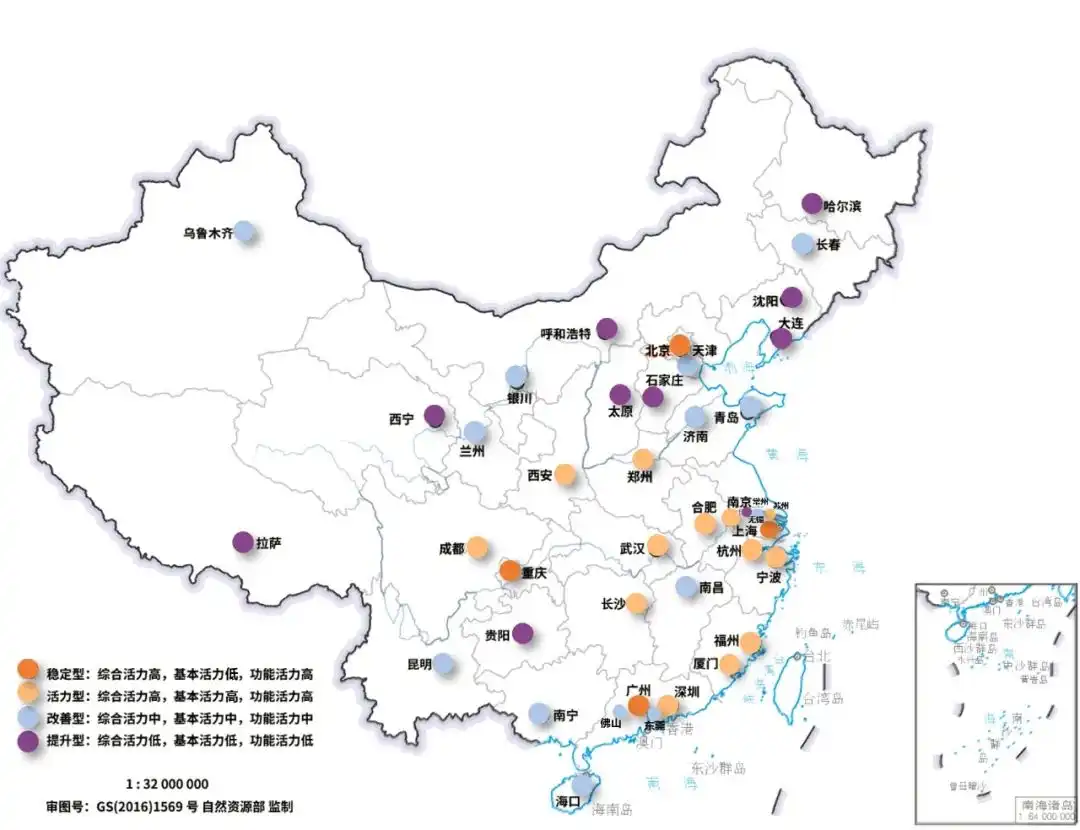
Top 10 Performing Arts Appreciation Recovery Index上海市、北京市、成都市、天津市、深圳市、杭州市、武汉市、重庆市、苏州市、广州市。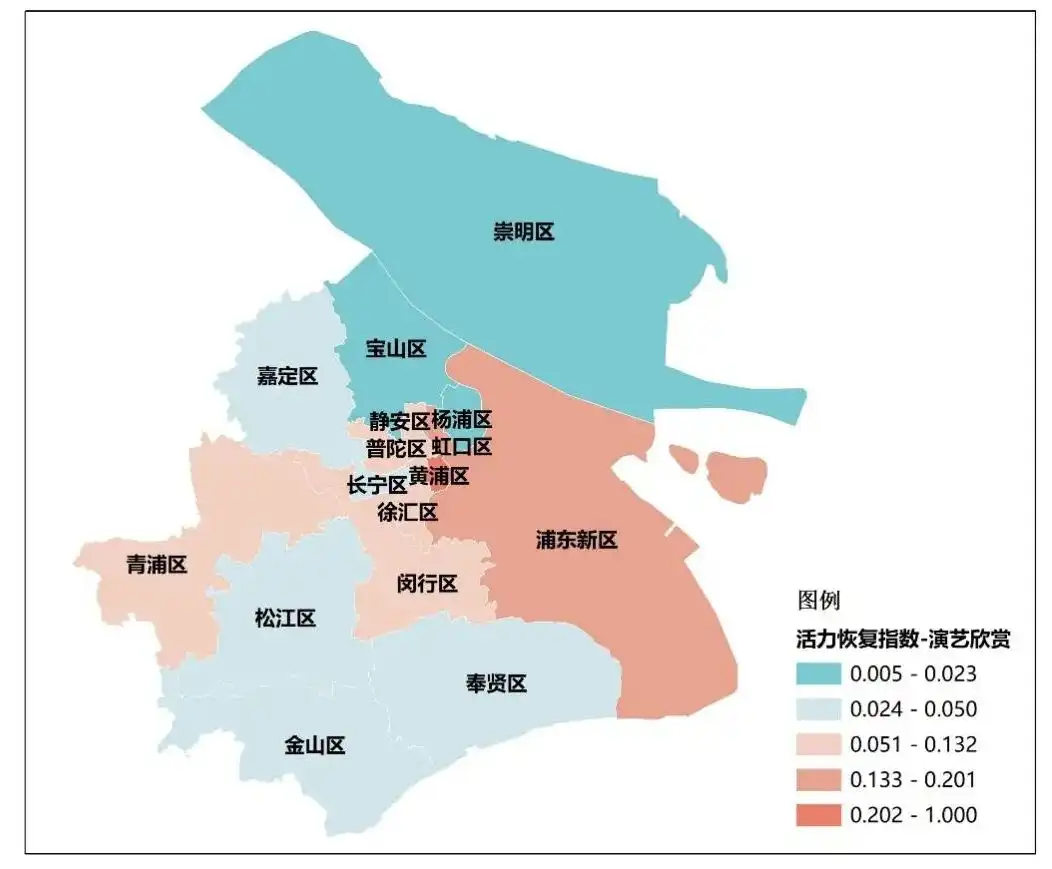 上海各区演艺欣赏类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
上海各区演艺欣赏类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
2021年,上海首批认定100家演艺新空间,涉及与音乐酒吧、茶楼、咖啡厅、酒店、购物中心、商圈广场、购物综合体、文创园区、书店、博物馆、展厅、商务楼宇等多种用地类型融合。通过将演艺空间和公共空间的深度结合,突破了传统表演艺术对场地的要求,有利于“全城戏剧”艺术氛围的构建,也有利于城市文化氛围的营造。
exhibition tour of:Wuhan,"City of Exhibition and Exhibition"
Exhibition visit recovery index Top 10武汉市、西安市、上海市、南京市、兰州市、成都市、银川市、长沙市、天津市、大连市。
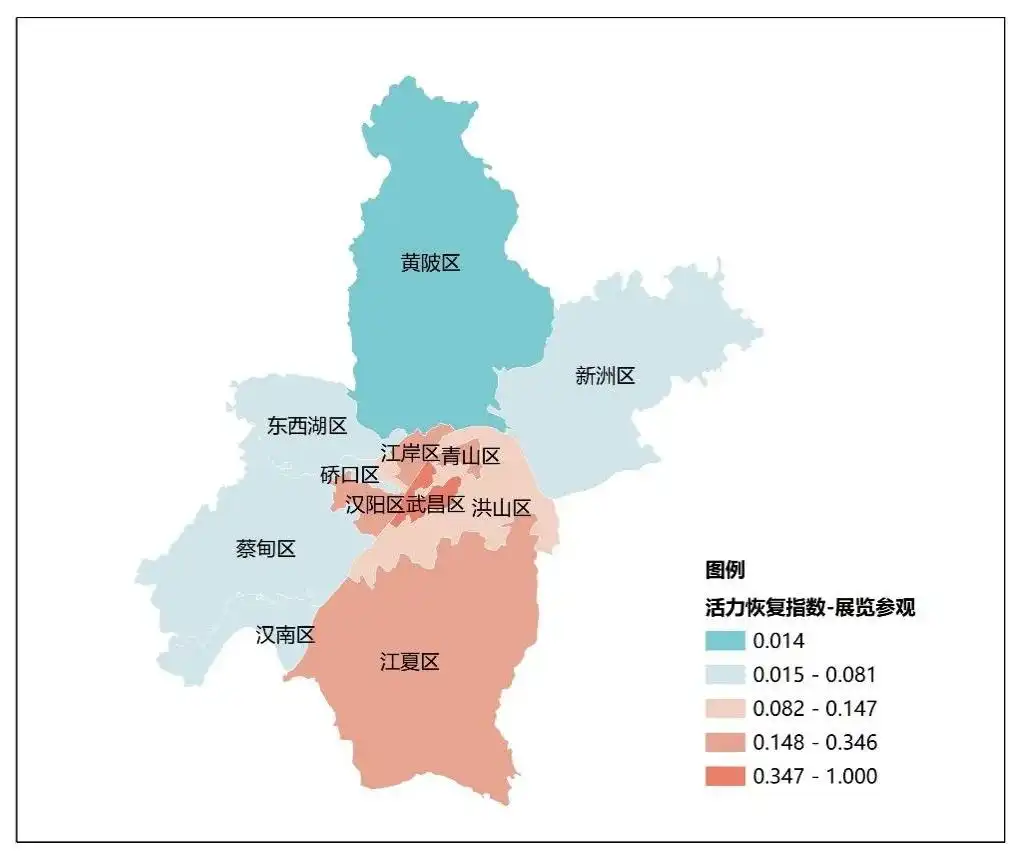
Vitality Recovery Index for exhibitions and visits in various districts in Wuhan ("2023 China's Urban Prosperity and Vitality Assessment Report" by the Chinese Academy of Planning)
Relying on its advantages in the thoroughfare of nine provinces, its strong economic scale and size, Wuhan strives to build a national exhibition center city with the help of rich education, science, culture, health, tourism and sports resources, distinctive specialized, special and new industry characteristics, and good business and exhibition policies. As of August 2023, Wuhan has held 653 exhibitions, festivals and events, a year-on-year increase of 77%(it is expected that there will be more than 1,000 exhibitions in 2023, the most in the past 10 years).
cultural landscape:Nanjing,"City of Museums"
Top 10 Cultural Landscape Restoration Index南京市、西安市、太原市、北京市、重庆市、大连市、杭州市、厦门市、沈阳市、哈尔滨市。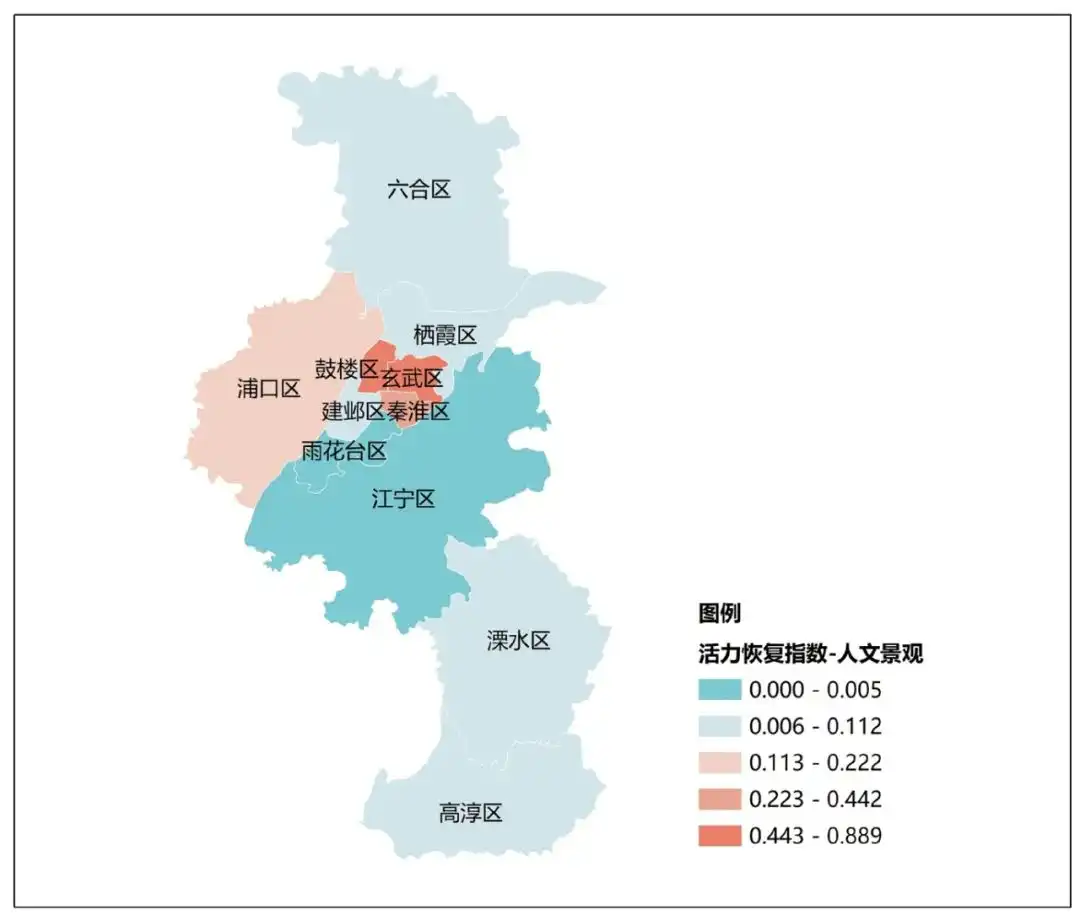 南京各区人文景观类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
南京各区人文景观类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
根据《南京市建设“博物馆之城”发展规划》目标,到2025年将力争新增100座备案注册博物馆,孵化100座类博物馆,每年举办展览300个以上。通过“博物馆+教育”“博物馆+社区”“博物馆+夜游”等多种模式文旅融合模式,将“文化展厅”升级为“文化客厅”。
natural landscape:Guiyang,"City of Thousands of Gardens"
Top 10 Natural Landscape Restoration Index贵阳市、南京市、北京市、石家庄市、成都市、太原市、重庆市、南宁市、杭州市、济南市。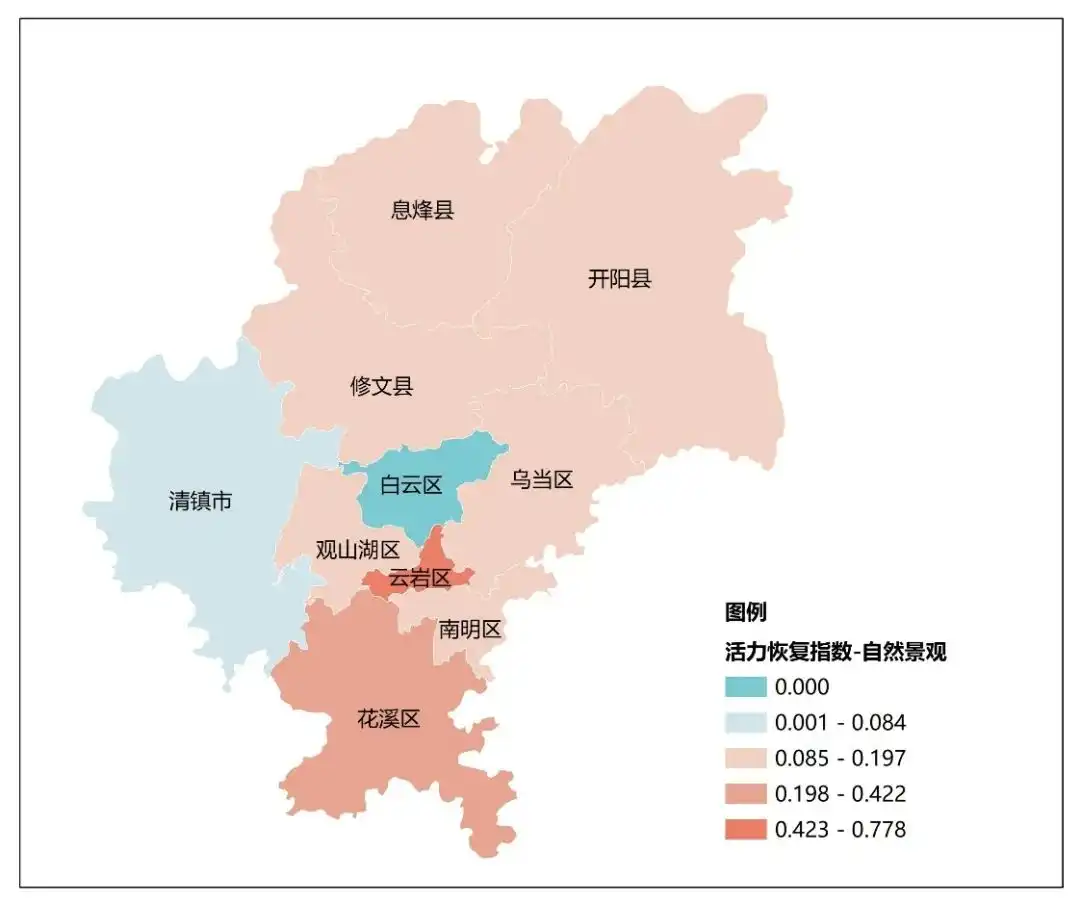 贵阳各区自然景观类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
贵阳各区自然景观类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
贵阳市近年来启动“千园之城”建设,大力新建森林公园、湿地公园、山体公园、城市公园、社区公园等各类公园。目前贵阳市各类公园总数达到1025个、人均公园绿地面积达14.85平方米,“300米见绿、500米见园”的城市公园格局基本形成。优越的生态环境成就了贵阳“中国避暑之都”的美誉,且上榜中国十大“大美之城”,入选“2023避暑旅游优选地”,登上“避暑度假推荐榜”榜首。
catering:Changsha, the city remembers new consumption
Top 10 catering recovery index长沙市、拉萨市、成都市、重庆市、青岛市、苏州市、西安市、南京市、杭州市、广州市。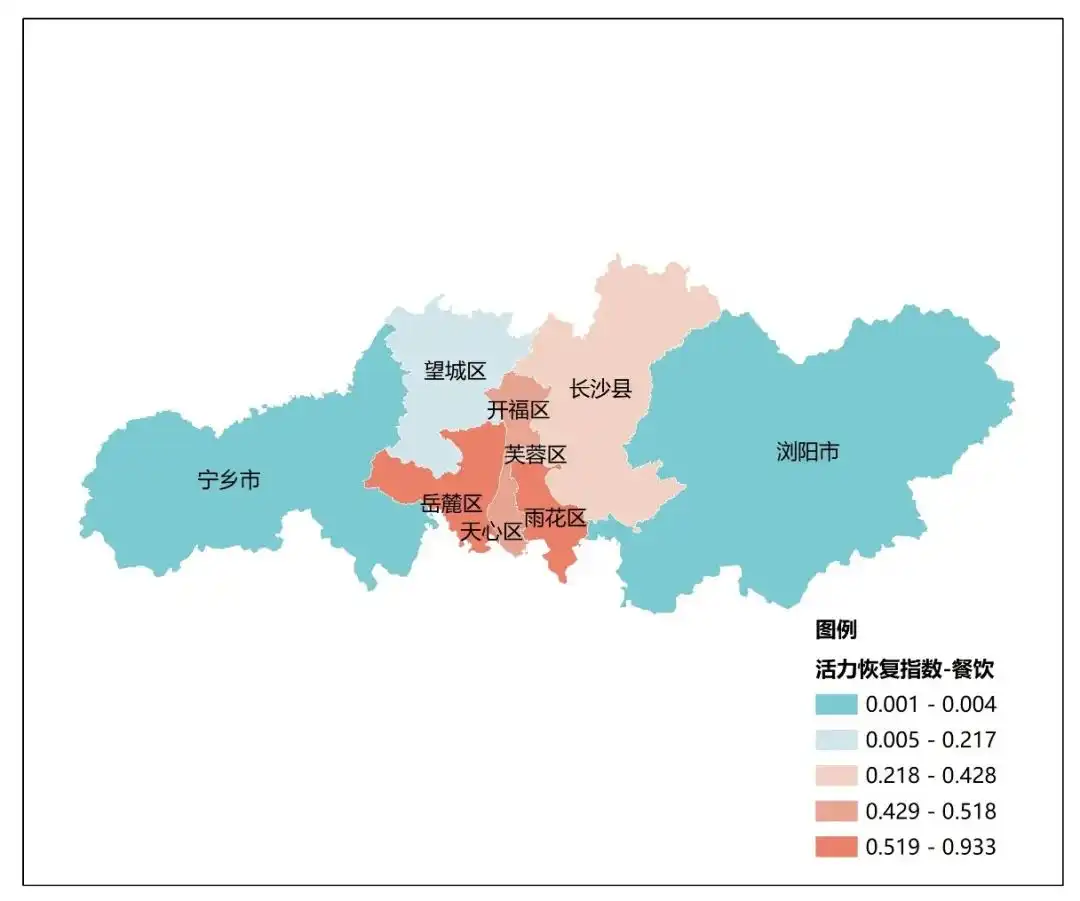 长沙各区餐饮类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
长沙各区餐饮类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
2018年3月以来,长沙市委、市政府在“旧城改造”中引入“有机更新”理念,在老城区5.6平方公里(合8400亩)范围内进行试点。坚持“保护+利用”原则,对白果园、西文庙坪、潮宗街等14处历史文化街区、历史地段(街巷)精准运用“留、改、拆、补”等办法,统筹推进有机更新,通过延续历史文脉、提升街区功能,为城市活力创造了更具记忆的消费场景。
bar:Chengdu, poetry and the distant night economy
Top 10 Bar Recovery Index成都市、长沙市、广州市、深圳市、重庆市、北京市、杭州市、西安市、上海市、拉萨市。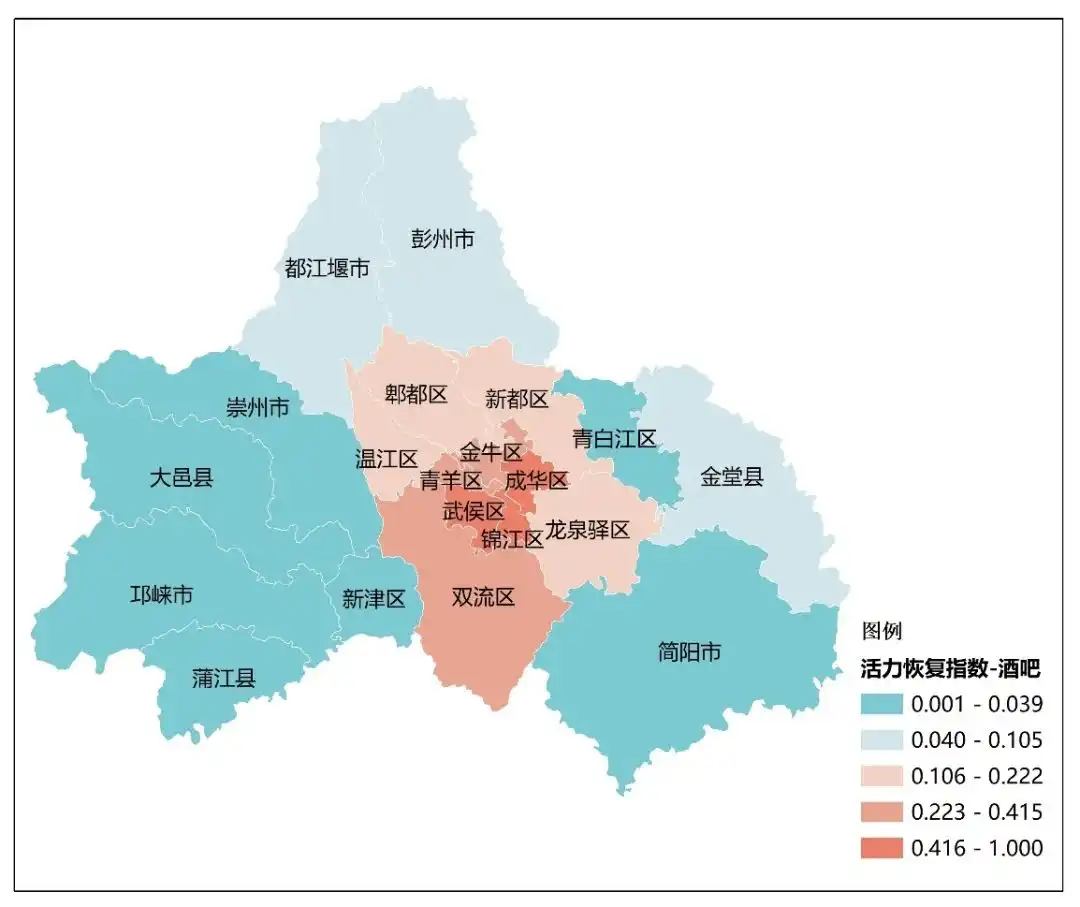 成都各区酒吧类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
成都各区酒吧类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
成都的夜间经济发展经历了从以美食和酒吧为主的1.0版,到融合艺术、文创、文博等新兴消费业态的2.0版,再到文商体旅深度融合、线上与线下一体化、科技与时尚交互共生的3.0 版。目前成都夜间消费规模占比达到45%,是典型的“以娱兴夜”型城市。酒吧作为成都夜间经济的中流砥柱,成都现有各类酒吧2500余家,数量排全国之首。
experience:Xi'an, ancient and modern national trend
Top 10 Experience Recovery Index成都市、西安市、长沙市、广州市、重庆市、苏州市、南京市、杭州市、深圳市、海口市。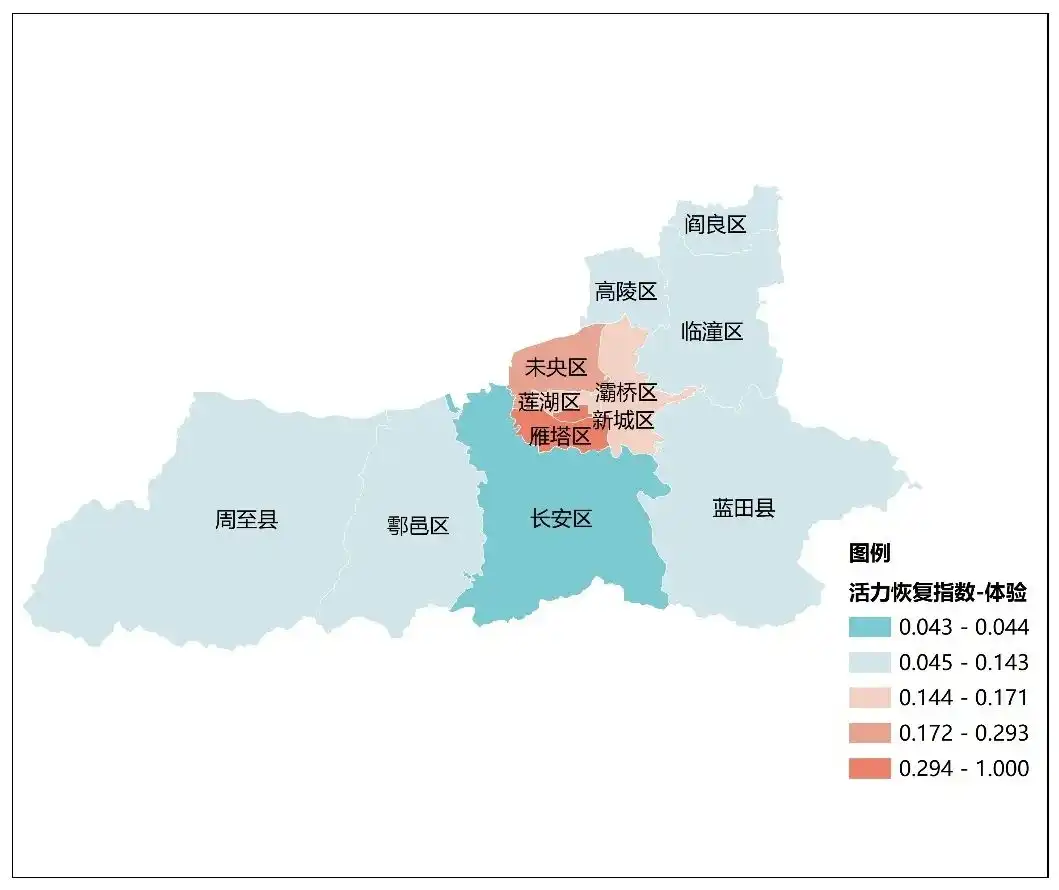 西安各区体验类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
西安各区体验类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
文化旅游产业是西安的支柱产业。为深化文化旅游供给侧结构性改革,西安大力发展沉浸式、 体验式新业态,聚焦历史文化、微度假、本地游、夜间经济,推动产品、场景、技术创新,构建特色化、品质化的文旅消费格局。当前西安已形成了从碑林历史文化街区、易俗社文化街区、小雁塔历史文化片区等大型综合文化街区,到长安书院、开元剧场、丝路欢乐世界、绿地丝路全球文化中心、西安曲江文创中心等中小型文旅空间,再到建国门老菜场、兴善寺西街、阳光天地等年轻人聚集的潮流地,到固定周末创意市集场地的多样化消费聚集地和多种规模的文旅吸引点。
leisure:Chongqing, Innovative Digital Entertainment
Top 10 Leisure Recovery Index长沙市、重庆市、西安市、兰州市、上海市、成都市、银川市、武汉市、拉萨市、长春市。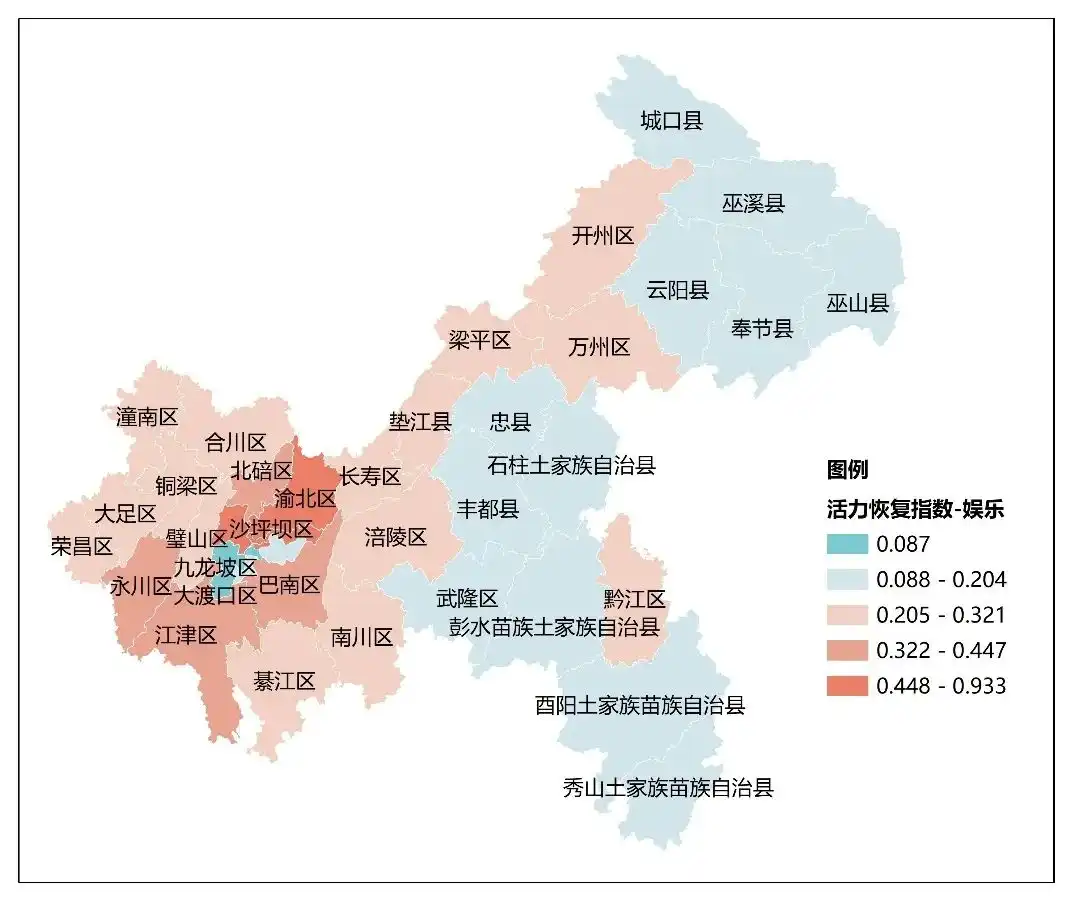 重庆各区休闲类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
重庆各区休闲类活力恢复指数(中规院《2023中国城市繁荣活力评估报告》)
Build a "consumption metaverse" scenario and a "cultural tourism metaverse" scenario. Promote the implementation of digital collections, digital art stores, digital content IP, etc. in shopping malls. Actively promote the vigorous development of the script entertainment industry and strive to create a new "script +" immersive entertainment consumption model. Seize the opportunity of live streaming to bring goods and continue to build more than 10 high-standard Live Video Broadcasting bases. Expand the new model of VR panoramic tourism, promote the integration of digital intelligence technology in cultural venues such as Chongqing Library, Chongqing Art Museum, Chongqing Industrial Culture Expo Park, Chongqing Grand Theater, and Three Gorges Museum, and accelerate the promotion of holographic imaging, augmented reality, 5G+8K and other technologies in book reading, cultural relics display and other fields are deeply integrated, promote the development of virtual performing arts events, and guide the combination of holographic projection, somatosensory interaction and other technologies with events, concerts, etc. Create a "super live" immersive experience that integrates hyper-digital reality.
Editorial board on duty:su Zhiyong
edit:Han Jianming
studying the:Dai Shichao