Evolution of the US military's maritime warfare concept:Return from sea control to three-dimensional attack and defense

In recent years, the United States has adjusted its focus to strategic competition and major power conflicts. With the rapid development of potential opponents 'medium and long-range missile weapon systems and the continuous enhancement of offshore control capabilities, the U.S. Department of the Navy officially proposed the "return to sea control" strategy, clarifying the strategic goal of surface forces returning to seizing sea control, triggering the U.S. Navy and Navy The Marine Corps combat concept is iteratively upgraded. By studying the evolution trend of the US military's maritime warfare concept, we will deeply analyze the new characteristics and changes in the US military's core maritime warfare ideas and the application of weapons and equipment, and explore the advantages and disadvantages of each combat concept, aiming to provide a tangible "target" for responding to high-end warfare in the maritime direction. Strengthen the pertinence and reliability of combat system and combat capability building.
From the Harrier aircraft carrier to the Lightning aircraft carrier
With the changes in maritime combat needs and the international situation, the U.S. Navy is facing increasingly severe challenges when projecting forces to areas of important interest, and flexible deployment and rapid response on a global scale have become the focus of attention. In recent years, the US Marine Corps has been considering transforming an amphibious assault ship into a light aircraft carrier, and has successively proposed combat concepts such as the Harrier aircraft carrier and the Lightning aircraft carrier from the perspective of a single ship.
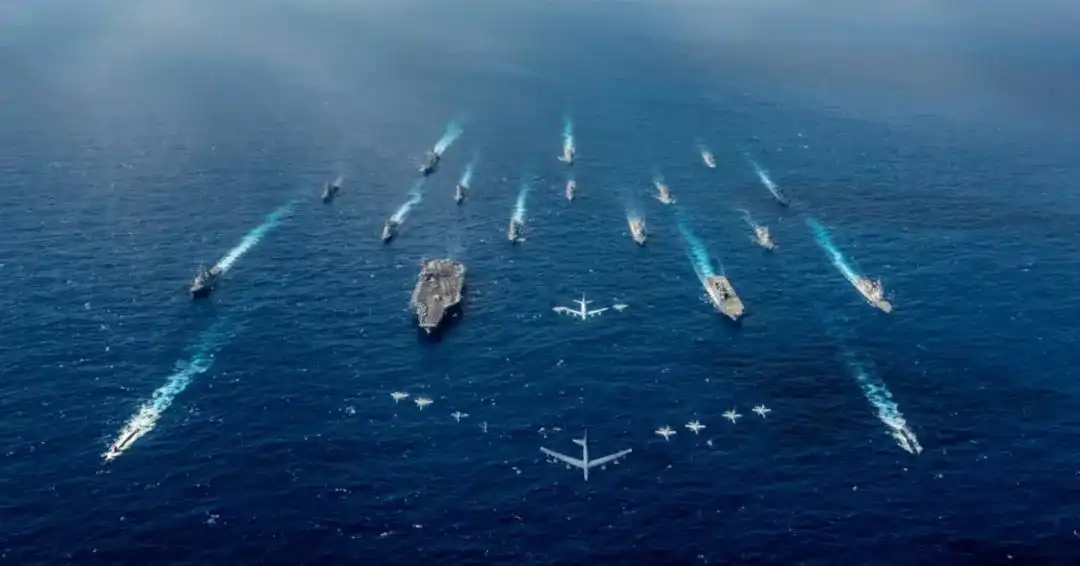
Harrier carrier 两栖攻击舰主要执行前沿部署、两栖登陆作战等任务,依靠搭载的武装直升机运载登陆力量,实施突击上陆作战,攻击滩头阵地、海岸纵深目标等,扫清作战对手陆地支援火力,为后续兵力顺利登陆创造条件。美军在设计建造黄蜂级两栖攻击舰时,就考虑了搭载短距/垂直起降战斗机的能力。伊拉克战争期间,黄蜂级两栖攻击舰LHD-5与LHD-6被指定为鹞式航母,各搭载20架AV-8B鹞式短距/垂直起降战斗机,无须接近滩头就能执行攻击任务,在对地支援和配合航母舰载机作战中发挥了重要作用。但AV-8B鹞式短距/垂直起降战斗机也存在明显不足,例如载弹量有限、作战半径较小、续航时间短等,正逐步被F-35B短距/垂直起降战斗机替代。

wasp-class amphibious assault ship
Lightning Aircraft Carrier 随着势均力敌对手陆续装备高性能岸基飞机、巡航导弹、弹道导弹、先进潜艇、无人机等装备,反介入/区域拒止体系的能力逐步增强。针对美军海上作战体系面临的威胁,海军陆战队将AV-8B鹞式短距/垂直起降战斗机更换为F-35B短距/垂直起降战斗机,两栖攻击舰的战斗力发生质的飞跃,达到中型航母的作战水平。
The lightning aircraft carrier combat concept was officially proposed in the "2017 US Marine Corps Aviation Construction Plan". The Lightning aircraft carrier allows the Navy's amphibious assault ship to carry the Marine Corps's F-35B short/vertical take-off and landing fighter jets and MV-22B tilt-rotor aircraft, greatly improving the amphibious assault ship's combat range and force delivery capabilities. The core idea of this combat concept is to make full use of the offshore combat advantages of amphibious assault ships to provide important entry, assembly and strike capabilities for the U.S. Navy and joint forces, and effectively enhance the flexibility, lethality and battlefield survivability of forward combat forces. The Lightning aircraft carrier has realized the transformation of amphibious assault ships from a force delivery platform to a light aircraft carrier combat application, and implemented three-dimensional attack operations in high-end warfare.
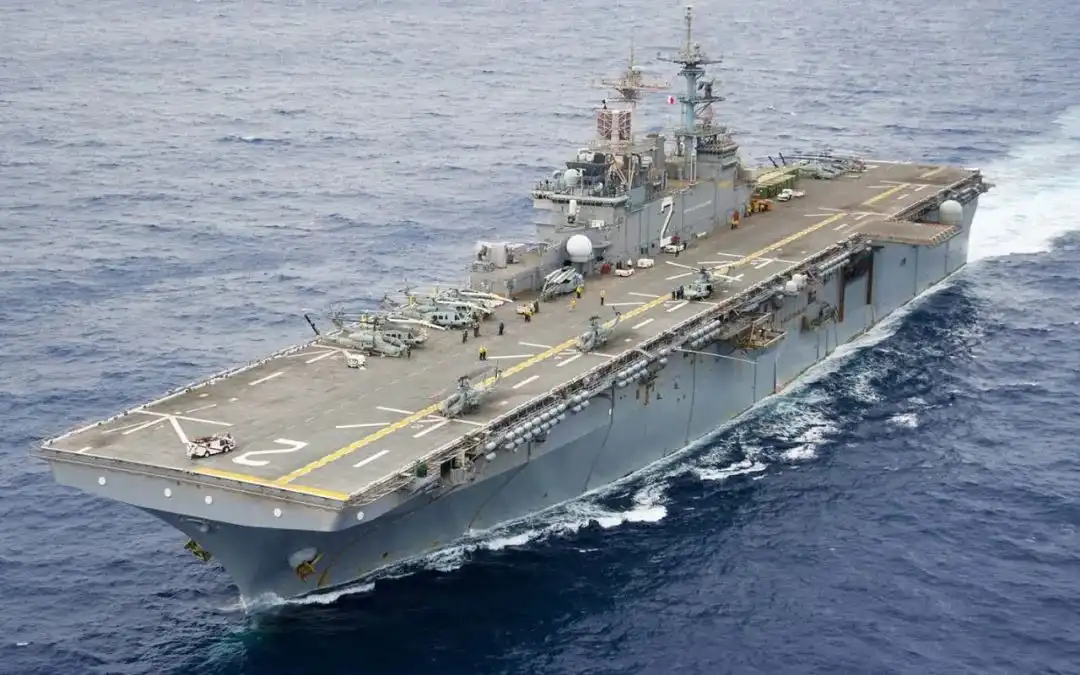
The Lightning aircraft carrier may become the development direction of the US military aircraft carrier, which will help alleviate the current shortage of naval forces and save a lot of military expenditures. In October 2017, RAND Corporation proposed in its "Future Aircraft Carrier Options" report:If the number of amphibious assault ships purchased is higher than the current aircraft carrier construction plan, it may be a low-risk alternative for the US Navy to reduce the cost of the aircraft carrier. It is recommended to replace the aircraft carrier with amphibious assault ships at a ratio of 2:1. The US military hopes to equip the amphibious assault ship with three F-35B fighter squadrons and adjust its combat application and organization methods to form a combat capability comparable to that of other countries 'medium-sized aircraft carriers, which can be used as a supplement to large aircraft carrier formations. In recent years, the US military has upgraded and modified five Wasp-class amphibious assault ships to carry more carrier-based aircraft. Among them, the Good Man Richard was retired due to a serious fire. Currently, two U.S. -class amphibious assault ships and four modified Wasp-class amphibious assault ships have the ability to carry F-35B fighter jets.

F-35B战斗机从The USS United States took off from the amphibious assault ship
Amphibious assault ships mainly carry out attack missions from sea to land. After upgrading and modification, they will be used as lightning aircraft carriers and will be difficult to adapt to future high-end wars. mainly manifested in four aspects:First, the F-35B short haul/vertical take-off and landing fighter jets have a limited number, carry less fuel and bombs, and have a short duration of combat, making it impossible to continuously perform high-intensity combat missions; second, it adopts a large open cabin design and is basically not resistant to sinking and is not suitable for carrying out sea-control combat missions; third, it cannot carry fixed-wing aircraft such as early warning aircraft, electronic warfare aircraft, and unmanned tankers that require ejection and take-off, and cannot perform combat missions independently in a strong confrontation battlefield environment; Fourth, it cannot sail at high speeds, and its ability to maneuver and evade attacks at sea is very limited.
From the Expeditionary Strike Group to the Fire-Enhanced Expeditionary Strike Group
At the beginning of the 21st century, the U.S. Marine Corps had 12 amphibious readiness brigades, each including a Wasp-class amphibious assault ship, a San Antonio-class dock transport ship, a Whidbey Island-class dock landing ship, and a land expedition team. In order to strengthen the combat capabilities of the amphibious readiness brigade, the US military has successively proposed combat concepts such as the Expeditionary Strike Brigade and the Fire-Enhanced Expeditionary Strike Brigade.
Expeditionary Strike Group 2003年,美海军提出以两栖攻击舰为核心的远征打击大队作战概念,应对以投送陆上武力为主的低强度作战。该作战概念就是在两栖戒备大队的基础上,增加1艘导弹巡洋舰、1艘导弹驱逐舰、1艘攻击型核潜艇等,兵力规模5000~6000人。目前,美海军有8个远征打击大队,分别是太平洋舰队的第1、3、5、7远征打击大队和舰队部队司令部的第2、4、6、8远征打击大队,其中第7远征打击大队驻扎于日本佐世保海军基地。
The Expeditionary Strike Group is a joint tactical grouping of the two services of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. It is the backbone of power projection from sea to land. It has strong capabilities in force projection, maritime attack and defense, and maritime control. It is the iron fist of landing operations. The core idea of the expeditionary strike group's operational concept is to give full play to the advantages of the amphibious assault ship's "sea base" and increase the defense capabilities of the "sea shield" and long-range "sea strike" capabilities. With the Air Force and Navy basically seizing air and sea supremacy, an expeditionary strike group can transport a combined battalion-sized force to quickly carry out amphibious landing operations, seize important strongholds near the coastline, and create conditions for landing operations and seizes beachhead positions to ensure that surface fleets can launch land strikes offshore.
Firepower enhanced version of the Expeditionary Strike Group 2016年4月,美军太平洋舰队司令提出火力加强版远征打击大队作战概念,就是由远征打击大队的两栖攻击舰搭载F-35B短距/垂直起降战斗机,逐步替代AV-8B鹞式短距/垂直起降战斗机。该作战概念整合了两栖攻击舰、F-35B短距/垂直起降战斗机、宙斯盾舰、攻击型核潜艇等力量,组成具备准航母编队能力的远征打击大队,将两栖戒备大队由登陆突击集群发展成为具备防空、反潜、反舰、对陆打击等能力的综合性海上作战集群。
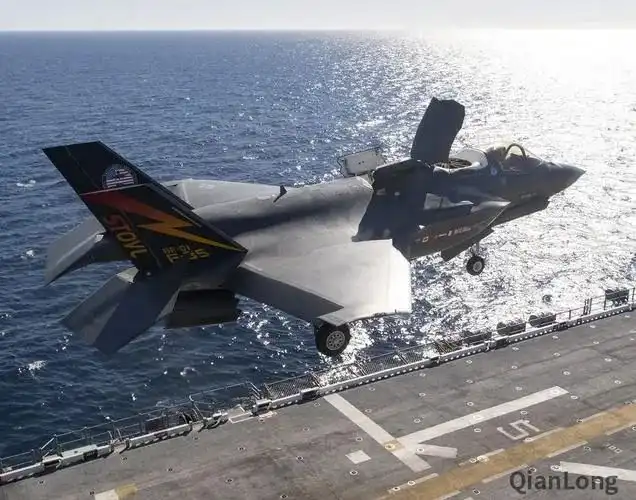

The delivery capabilities, firepower, and air defense combat capabilities of the enhanced firepower version of the Expeditionary Strike Brigade have been strengthened
The enhanced firepower version of the Expeditionary Strike Group's combat concept focuses on improving the offensive combat capabilities of the amphibious assault ship formation. It is equipped with one F-35B fighter squadron, usually six. This has greatly enhanced the expeditionary strike group's capabilities of ocean control, sea strike and land strike, and improved the flexibility of the use of maritime forces. The combat radius has been expanded from 400 kilometers to 800 kilometers, with the ability to conduct high-end wars. The amphibious assault ship is equipped with F-35B short/vertical take-off and landing fighters, MV-22B tilt-rotor aircraft and MH-60S helicopters to transport the Marine Expeditionary Force and Naval Special Forces to independently carry out strategic and tactical strike missions, or support the US military in seizing air and sea supremacy, force delivery, amphibious landing, underwater operations and even electromagnetic warfare.
Based on the U.S. Navy's current number of amphibious squadrons, land expeditionary teams, fighter jets, etc., the U.S. military can organize seven fire-enhanced expeditionary strike groups. In recent years, the US military has repeatedly deployed F-35B short/vertical take-off and landing fighters to Japan's Iwakuni Sea Terminal, Sasebo Naval Base, etc. These fighters can take off from land or amphibious assault ships. The US military is exploring the implementation of distributed maritime operations through a fire-enhanced version of the Expeditionary Strike Brigade. The combat area is gradually expanding from offshore and near-shore to the entire region and all areas. The combat tasks are gradually changing from sending troops from sea to land to sending troops from sea to land. Specific operational styles include amphibious operations, operations to gain and maintain maritime superiority, land-strike operations, and other maritime operations.
The enhanced firepower version of the Expeditionary Strike Group has outstanding combat capabilities:First, it has strong three-dimensional delivery capabilities. Relying on the amphibious assault ship to establish a forward base, and with the support and cover of F-35B fighter jets, the forces they carry are quickly delivered to sea and air. Second, it has strong firepower support capabilities. This combat concept integrates a variety of advanced sea, land and air combat platforms, greatly improving the capabilities of air supremacy operations, long-range precision strikes, and fire cover landing. Third, it has strong air defense combat capabilities. Relying on the coordination of surface ships and carrier-based aircraft, it forms an air defense barrier from far to near to ensure the smooth implementation of landing operations and the preservation of combat strength. However, the enhanced firepower version of the Expeditionary Strike Group has weak capabilities in stealth, anti-submarine warfare, and anti-mine warfare.
From expeditionary forward base operations to coastal operations in a confrontational environment
In high-end wars, the Marine Corps 'forward deployment faces huge threats, and it is difficult to cope with various emergencies when its forces withdraw. Under the guidance of the idea of distributed warfare, the Marine Corps regards the coastal region as a whole, explores the use of cross-domain forces and cross-service command and control issues, and successively proposes concepts such as coastal warfare in the combat confrontation environment of expeditionary forward bases. These concepts and the concept of distributed maritime warfare proposed by the Navy rely on each other to jointly support high-end warfare at sea.
Expeditionary Forward Base Operations 2016年9月,美海军陆战队司令部发布顶层设计文件《21世纪远征部队作战》,提出远征前进基地作战概念,要求建立分散、机动的前沿军事基地,以形成一个持久的能力场,提供强大的战场生存能力。该概念旨在增强海军陆战队在西太平洋地区的作战能力,在反进入/区域拒止体系威胁的近岸海域,利用广泛分布、数量众多的岛屿,海军陆战队岸基作战力量与海军作战力量协同夺取局部海域控制权。
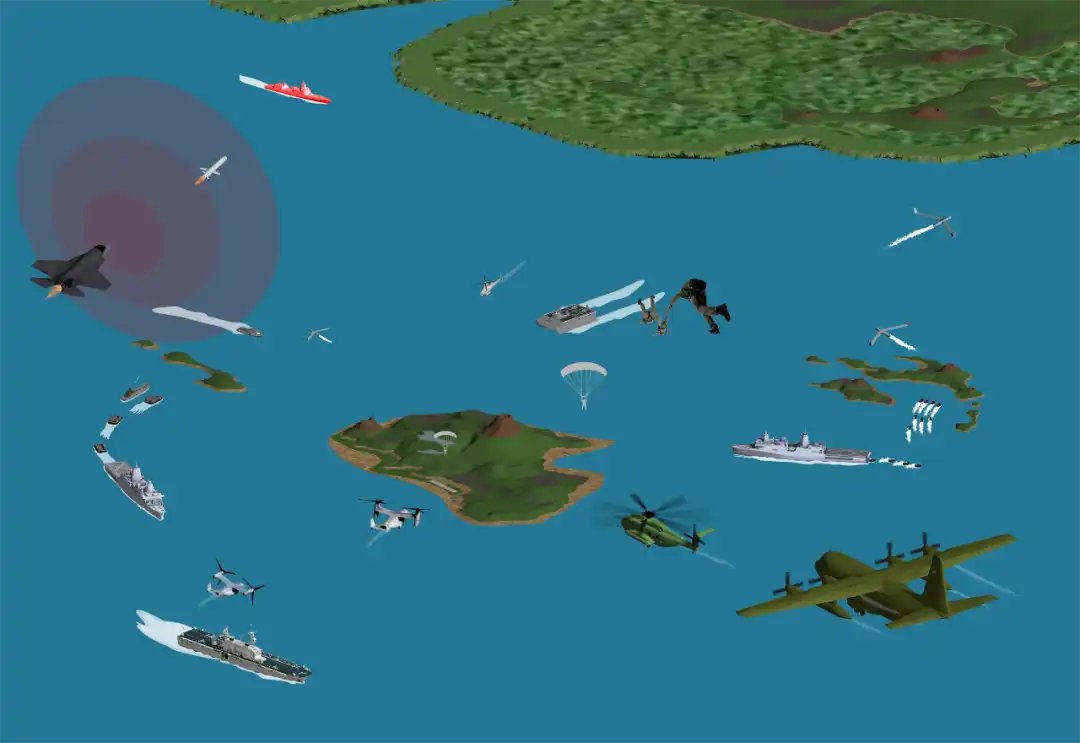

Schematic diagram of the operational concept of the expeditionary forward base
The core idea of the expeditionary forward base combat concept is to use a variety of air and surface platforms to quickly and discretely deliver small-scale troops and equipment with anti-zone strike capabilities to the forward islands of the theater, and use distributed long-range precision firepower to form dense kill zones., destroy surface and even land targets of combat opponents. The expeditionary advance bases are scattered and can be deployed on shore, coastal and archipelago waters, inland lakes and rivers; they can also be deployed on light amphibious warships, littoral combat ships, bulk carriers, barges, etc., greatly improving battlefield survivability. The expeditionary advance base is not a specific location or area, but a collection of distributed support capabilities. It has certain defensive capabilities, which can not only deter possible strikes by opponents, but also greatly increase the difficulty of intelligence, reconnaissance, tracking and strikes by opponents.
The expeditionary forward base combat concept uses a large number of islands and reefs controlled by allies to strategically defend and tactically attack. It is a new style of expeditionary warfare. In peacetime, the Land Expeditionary Force is deployed in confrontational or potential confrontational sea, shore or coastal areas. It has the advantages of high mobility, low characteristics, and ease of maintenance, and can be used as a deterrent. In wartime, the Marine Expeditionary Force carried out tasks such as maritime blockade, competition for sea power, and fleet supply to support the projection of naval power to the forefront. The expeditionary forward base operating concept will give fleet commanders and joint maritime operations commanders a wider range of integrated maritime power options, as well as more sensors, weapon systems and other resources.
The operational concept of the expeditionary forward base focuses on a specific combat environment, targets specific opponents and typical combat attempts, and has strong directivity, but it also has obvious shortcomings. First, it is difficult for large surface ships to survive. Large amphibious ships such as amphibious assault ships and dock transport ships serve as delivery platforms and face the threat of precision strikes by anti-ship missiles when close to opponents 'waters. Second, the combat process is complex. The Marine Corps requires external information support, is difficult to interoperate with the Navy, and has limited collaborative combat capabilities. It needs to establish complex command relationships to support command operations and combat control. Third, maritime communication lines are vulnerable to attacks. Logistics support forces are vulnerable to attacks by long-range missiles, torpedoes and mines, resulting in a sharp decline in the ability to sustain forward operations. Fourth, political and diplomatic resistance is great. Relying on the islands, reefs and military and civilian facilities of allies and partners at the forefront, it is necessary to obtain authorization to enter their territorial waters and airspace, forcing relevant countries to choose sides in high-end wars and increasing the uncertainty that the US military will gain forward support points.
Coastal operations in a confrontational environment 随着作战对手陆续部署先进导弹,海战与陆战的界限变得模糊。2017年10月,美海军作战部长、海军陆战队司令联合签署发布《对抗环境中濒海作战》,提出对抗环境中濒海作战概念。该概念将海军陆战队的海基、陆基能力纳入制海作战行动,强调海军与海军陆战队实施一体化海上作战、陆上作战与海陆双向作战。
The core idea of the concept of coastal warfare in a confrontational environment is to gather all combat units in the region into the same command system to enhance the commander's crisis handling capabilities and response speed. The concept provides a continuously mobile cutting-edge presence to respond to crises or large-scale armed conflicts by creating a modular, scalable, and integrated maritime combat network composed of sea-based and land-based sensors, weapon systems, support resources, etc. The U.S. Navy and Marine Corps have established a Littoral Combat Group with sea-control combat capabilities. It mainly includes an amphibious readiness group and a land expeditionary team, with capabilities such as surface combat, underwater combat and expeditionary mine warfare.
The U.S. military attempts to rely on integrating the command systems of the Navy and Marine Corps to create an integrated fleet and joint force maritime commander staff headquarters. The Navy flagship commander serves as the commander, and the Navy and Marine Corps integrated staff headquarters implements operational planning to offset opponents 'combat advantages in a littoral confrontation environment. Compared with the expeditionary forward base combat concept, this concept is hindered by the interests of the services, and its shortcomings are more obvious and it is difficult to implement in a short period of time.
From distributed kill to distributed maritime operations
In response to cutting-edge military threats, the US Navy put forward the idea of "fighting every ship and dividing troops and concentrating fire" in an attempt to achieve the effect of dispersion in space and concentration in efficiency. The U.S. Navy has successively proposed the concept of distributed antipersonnel operations and the concept of distributed maritime operations. The concept of distributed maritime operations has been jointly supported by the Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard, and has become the current top-level combat concept of the U.S. Navy.
distributed kill 2014年底,针对水面舰船反舰能力不足的问题,美海军战争学院在兵棋推演中创新运用濒海战斗舰,提出分布式杀伤作战概念。2015年1月,美海军水面部队司令、大西洋舰队水面部队司令与海军部水面作战局局长在《美海军水面部队战略》中提出分布式杀伤作战概念,强调提升水面部队的反舰能力,应对潜在对手日益增强的反进入/区域拒止体系威胁。该作战概念是全球公域进入与机动联合战略框架下对水面舰艇作战模式的一种新尝试,成为美海军实现与保持制海能力的重要措施。
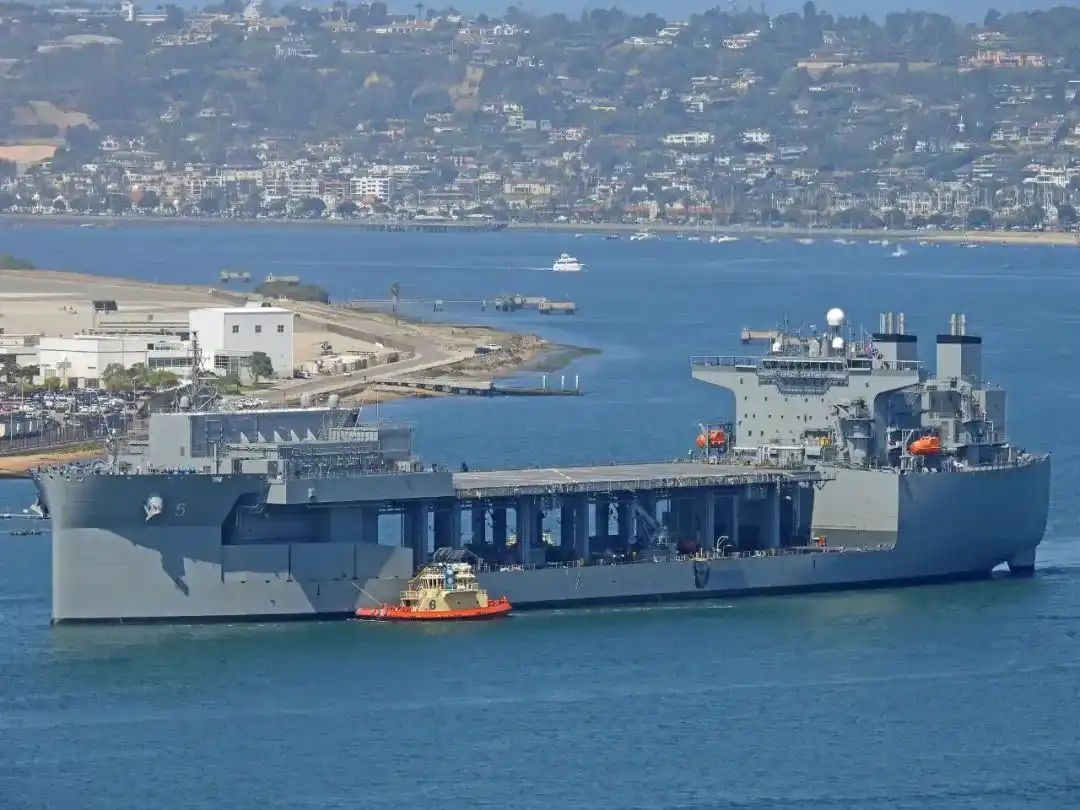

US Navy Expeditionary Floating Base Ship
The core idea of the concept of distributed kill warfare is to decompose some weapons, sensors, electromagnetic warfare and other functions of large and medium-sized surface ships into small and medium-sized surface ships through an open architecture and a networked information transmission system, and operate independently in the form of decentralized deployment. Achieve stronger combat capabilities through autonomous, collaborative and other technologies, mainly including single-platform offensive kill capabilities, decentralized deployment and flexible mobility across a wide geographical area, and multi-platform collaborative defense capabilities. Increase the number of targets that opponents need to deal with and increase the difficulty of target positioning and decision-making. It can be seen that distributed killing has obvious system complexity and vulnerability.
The concept of distributed kill warfare emphasizes enhancing the offensive and defensive capabilities of surface ships and implementing surface operations through wide-area decentralization and dynamic deployment. From an offensive perspective, distributed killing achieves flexible strikes with long-range precision firepower through decentralized deployment, multi-point launches, and concentrated damage, improves the lethality of surface troops, and increases the difficulty of defense against combat opponents. The main combat operations include reconnaissance deterrence, network and electricity Interference, offensive power grab, heavy hammer assault, containment and blockade, etc. From a defensive perspective, distributed kill exerts saturation pressure on the combat opponent's forward reconnaissance and surveillance systems. The opponent's C4ISR system cannot carry out continuous reconnaissance and surveillance on the US military combat platform, reducing the possibility of surface ships being detected, locked in and attacked, thereby improving the battlefield survivability of surface ships.
Distributed maritime operations 在继承与发展分布式杀伤作战概念的基础上,美海军于2016年发布《保持海上优势的战略设计》,提出分布式海上作战概念。2018年12月,美海军作战部长约翰·理查德森上将签发战略文件《维持海洋优势的设计2.0》,强调分布式海上作战是美海军针对作战对手开发的军种顶层作战概念。该战略文件将分布式海上作战定义为:“在选择的时间和地点,充分利用分布式、一体化与机动性原则,取得大规模压倒性作战力量与作战效果。这种分布式平台、武器、系统与传感器的集成,不仅可以提高战场态势感知能力,还可使作战对手的侦察工作复杂化。在领域范围内机动运用作战力量,利用不确定性实现突袭。”
The core idea of the concept of distributed maritime operations is to achieve difficult to be found, difficult to be attacked and highly lethal by rejecting the intelligence surveillance and reconnaissance of combat opponents and distributed troops. The concept innovates the force formation mode, and the main changes are shown in two aspects. First, the combat force has changed from a surface warship force to an all-sea force. Focusing on large-scale combat at the fleet level, various forces are dispersed and deployed in space, sea and air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic space. Not only surface forces such as aircraft carriers, surface action groups, and amphibious garrison groups participate in combat, cruise missile nuclear submarines, Fmur35 fighters and other underwater and air forces can also participate in the war, realizing the joint use of all maritime forces. Reconnaissance and surveillance of vast sea areas in peacetime, and anti-ship, anti-submarine, air defense, land-to-land attacks and other combat tasks in wartime. Second, the scope of operations has changed from the surface of the water to the entire theater. Distributed maritime operations extend surface operations to multi-domain operations, obtain more information and resources within the theater, provide third-party sensor information to fire strike platforms, and achieve "detection forward", "strike forward" and "defense forward". Fight for comprehensive control of sea and air in the western Pacific.
Conclusion
Exploring the evolution of the US military's maritime warfare concept, it is not difficult to find that the maritime direction will become an important area for the US military to prepare for high-end wars. From the perspective of combat strength, amphibious assault ships and F-35B short/vertical take-off and landing fighters will play an important role in sea-direction operations. Building an agile adaptive kill chain to attack amphibious assault ships and F-35B will be useful for defeating the US military. The maritime combat system is of great significance. Restricted by factors such as allies and partners choosing sides and the balance of interests among various US military services, the implementation and future implementation of the concept of maritime warfare face many uncertainties. From the perspective of the combat system, the US military's maritime combat system is multi-faceted, and there are still a large number of high-value nodes in the frontier waters. The new combat concept not only increases the complexity of the combat system, but also increases the vulnerability of the system, allowing opponents to implement the system. Break provides an opportunity.
copyright notice:This article was published in the 2nd issue of Military Digest magazine in 2024. The author:Song Zhifeng, Xue Xingtang, etc., If you need to reprint it, please be sure to indicate "Transferred from Military Digest".
attention to our